Page 69 - GPD-1-2
P. 69
Gene & Protein in Disease Recent advances and challenges of network biology
A
B C
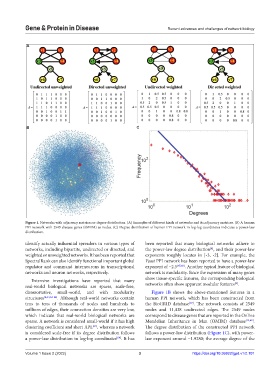
Figure 1. Networks with adjacency matrices or degree distribution. (A) Examples of different kinds of networks and its adjacency matrices. (B) A human
PPI network with 2549 disease genes (OMIM) as nodes. (C) Degree distribution of human PPI network in log-log coordinates indicates a power-law
distribution.
identify actually influential spreaders in various types of been reported that many biological networks adhere to
networks, including bipartite, undirected or directed, and the power-law degree distribution , and their power-law
[4]
weighted or unweighted networks. It has been reported that exponents roughly locates in [-3, -2]. For example, the
SpectralRank can also identify functional important global Yeast PPI network has been reported to have a power-law
regulator and command interneurons in transcriptional exponent of −2.5 [65,66] . Another typical feature of biological
networks and neuron networks, respectively. network is modularity. Since the expression of many genes
Extensive investigations have reported that many show tissue-specific features, the corresponding biological
[4]
real-world biological networks are sparse, scale-free, networks often show apparent modular features .
disassortative, small-world, and with modularity Figure 1B shows the above-mentioned features in a
structures [4,13,62-64] . Although real-world networks contain human PPI network, which has been constructed from
tens to tens of thousands of nodes and hundreds to the BioGRID database . The network consists of 2549
[67]
millions of edges, their connection densities are very low, nodes and 11,438 undirected edges. The 2549 nodes
which indicate that real-world biological networks are correspond to disease genes that are reported in the Online
sparse. A network is considered small-world if it has high Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) database [13,68] .
clustering coefficient and short APL , whereas a network The degree distribution of the constructed PPI network
[63]
is considered scale-free if its degree distribution follows follows a power-law distribution (Figure 1C), with power-
a power-law distribution in log-log coordinates . It has law exponent around −1.9280; the average degree of the
[64]
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.v1i2.101