Page 72 - GPD-1-2
P. 72
Gene & Protein in Disease Recent advances and challenges of network biology
A
B
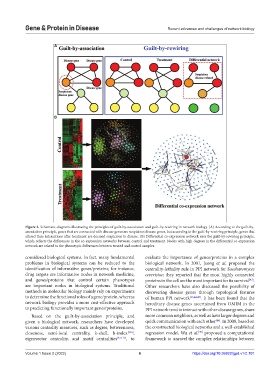
Figure 3. Schematic diagrams illustrating the principles of guilt-by-association and guilt-by-rewiring in network biology. (A) According to the guilt-by-
association principle, genes that are connected with disease genes are suspicious disease genes, but according to the guilt-by-rewiring principle, genes that
altered their interactions after treatment are deemed suspicious to disease. (B) Differential co-expression network uses the guilt-by-rewiring principle,
which reflects the differences in the co-expression networks between control and treatment. Nodes with high degrees in the differential co-expression
network are related to the phenotypic differences between treated and control samples.
considered biological systems. In fact, many fundamental evaluate the importance of genes/proteins in a complex
problems in biological systems can be reduced to the biological network. In 2001, Jeong et al. proposed the
identification of informative genes/proteins; for instance, centrality-lethality rule in PPI network for Saccharomyces
drug targets are informative nodes in network medicine, cerevisiae; they reported that the most highly connected
and genes/proteins that control certain phenotypes proteins in the cell are the most important for its survival .
[43]
are important nodes in biological systems. Traditional Other researchers have also discussed the possibility of
methods in molecular biology mainly rely on experiments discovering disease genes through topological features
to determine the functional roles of a gene/protein, whereas of human PPI network [13,44,45] . It has been found that the
network biology provides a more cost-effective approach hereditary disease genes ascertained from OMIM in the
to predicting functionally important genes/proteins. PPI network tend to interact with other disease genes, share
Based on the guilt-by-association principle, and more common neighbors, as well as have larger degrees and
[44]
given a biological network, researchers have developed quick communication with each other . In 2008, based on
various centrality measures, such as degree, betweenness, the constructed biological networks and a well-established
closeness, semi-local centrality, k-shell, h-index [116] , regression model, Wu et al. proposed a computational
[45]
eigenvector centrality, and motif centralities [47,117] , to framework to unravel the complex relationships between
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.v1i2.101