Page 94 - GPD-1-2
P. 94
Gene & Protein in Disease Structure and function of USP7
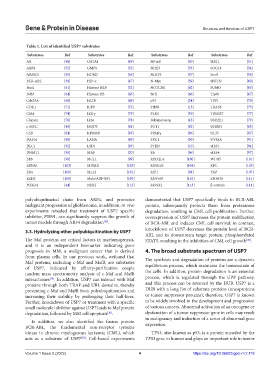
Table 1. List of identified USP7 substrates
Substrates Ref Substrates Ref Substrates Ref Substrates Ref
AR [48] GATA1 [49] NF-ĸB [50] SIRT1 [51]
ARF4 [52] GMPS [32] NHE3 [53] SOCS1 [54]
ARMC5 [55] HDM2 [56] NLRP3 [57] So×9 [58]
BCR-ABL [38] HIF-α [47] N-Myc [59] SPRTN [60]
Bmi1 [61] Histone H2B [32] NOTCH1 [62] SUMO [63]
Bub3 [64] Histone H3 [65] Nrf1 [66] Tip60 [67]
Cdc25A [68] HLTF [69] p53 [24] TPP1 [70]
CDK1 [71] ICP0 [72] PHF8 [15] TRAF6 [73]
Chk1 [74] IKKγ [75] PLK1 [76] TRIM27 [77]
Clapsin [76] IRSs [78] Polymerase η [45] UbE2E1 [79]
c-MYC [80] JMJD3 [81] POT1 [82] UHRF1 [83]
CSB [84] KDM6B [85] PPARγ [86] UL35 [87]
DAF16 [88] LANA [89] PRC1 [90] UVSSA [91]
DLC1 [92] LSD1 [93] PTEN [10] vIRF1 [94]
DNMT1 [95] MAF [20] Rb [96] vIRF4 [97]
E1B [98] MCL1 [99] RECQL4 [100] WDR5 [101]
EBNA1 [102] MDMX [103] RING1B [104] XPC [105]
ERα [106] MLL2 [101] RIP1 [98] YAP [107]
EZH2 [108] Mule/ARF-BP1 [109] RNF168 [110] ZNF638 [111]
FOXO4 [44] NEK2 [112] RUNX2 [113] β-catenin [114]
polyubiquitinated chain from ARF4, and promotes demonstrated that USP7 specifically binds to BCR-ABL
malignant progression of glioblastoma. In addition, in vivo protein, subsequently protects them from proteasome
experiments revealed that treatment of USP7 specific degradation, resulting in CML cell proliferation. Further,
inhibitor, P5091, can significantly suppress the growth of overexpression of USP7 increases the protein stabilization
tumor models through ARF4 degradation . of BCR-ABL and induces CML cell survival; in contrast,
[52]
knockdown of UPS7 decreases the protein level of BCR-
3.3. Hydrolyzing other polyubiquitination by USP7
ABL and its downstream target protein, phosphorylated
The Maf proteins are critical factors in myelomagenesis, STAT5, resulting in the inhibition of CML cell growth .
[38]
and it is an independent biomarker indicating poor
prognosis in MM, a malignant cancer that is derived 4. The broad substrate spectrum of USP7
from plasma cells. In our previous work, wefound that The synthesis and degradation of proteins are a dynamic
Maf proteins, including c-Maf and MafB, are substrates
of USP7, indicated by affinity-purification couple equilibrium process, which maintains the homeostasis of
tandem mass spectrometry analysis of c-Maf and MafB the cells. In addition, protein degradation is an essential
interactomes . In addition, USP7 can interact with Maf process, which is regulated through the UPP pathway,
[20]
proteins through both TRAF and UBL domains, thereby and this process can be reversed by the DUB. USP7 is a
preventing c-Maf and MafB from polyubiquitination and DUB with a long list of substrate proteins (oncoproteins
increasing their stability by prolonging their half-lives. or tumor suppressor proteins); therefore, USP7 is known
Further, knockdown of USP7 or treatment with a specific to be widely involved in the development and progression
small molecule inhibitor against USP7 leads to Maf protein of various cancers. Abnormal activation of an oncogene or
[20]
degradation, followed by MM cell apoptosis . dysfunction of a tumor suppressor gene in cells may result
in malignancy and induction of a series of abnormal gene
In addition, we also identified the fusion protein
BCR-ABL, the fundamental non-receptor tyrosine expression.
kinase in chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), which TP53, also known as p53, is a protein encoded by the
acts as a substrate of USP7 . Cell-based experiments TP53 gene in human and plays an important role in tumor
[38]
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.v1i2.118