Page 32 - GPD-3-1
P. 32
Gene & Protein in Disease Natural carotenoids prevent prostate cancer
A
B
C
D
E
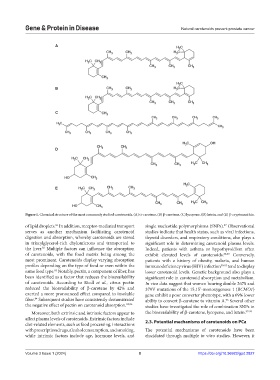
Figure 1. Chemical structure of the most commonly studied carotenoids. (A) α-carotene, (B) β-carotene, (C) lycopene, (D) lutein, and (E) β-cryptoxanthin.
of lipid droplets. In addition, receptor-mediated transport single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Observational
87
81
serves as another mechanism facilitating carotenoid studies indicate that health status, such as viral infections,
digestion and absorption, whereby carotenoids are stored thyroid disorders, and respiratory conditions, also plays a
in triacylglycerol-rich chylomicrons and transported to significant role in determining carotenoid plasma levels.
the liver. Multiple factors can influence the absorption Indeed, patients with asthma or hypothyroidism often
82
of carotenoids, with the food matrix being among the exhibit elevated levels of carotenoids. 88,89 Conversely,
most prominent. Carotenoids display varying absorption patients with a history of obesity, malaria, and human
profiles depending on the type of food or even within the immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection 90-95 tend to display
same food type. Notably, pectin, a component of fiber, has lower carotenoid levels. Genetic background also plays a
83
been identified as a factor that reduces the bioavailability significant role in carotenoid absorption and metabolism.
of carotenoids. According to Riedl et al., citrus pectin In vivo data suggest that women bearing double 267S and
reduced the bioavailability of β-carotene by 42% and 379V mutations of the 15,15’-monoxygenase 1 (BCMO1)
exerted a more pronounced effect compared to insoluble gene exhibit a poor converter phenotype, with a 69% lower
fiber. Subsequent studies have consistently demonstrated ability to convert β-carotene to vitamin A. Several other
84
96
the negative effect of pectin on carotenoid absorption. 85,86 studies have investigated the role of combination SNPs in
Moreover, both extrinsic and intrinsic factors appear to the bioavailability of β-carotene, lycopene, and lutein. 97-99
affect plasma levels of carotenoids. Extrinsic factors include 2.3. Potential mechanisms of carotenoids on PCa
diet-related elements, such as food processing, interactions
with prescription drugs, alcohol consumption, and smoking, The potential mechanisms of carotenoids have been
while intrinsic factors include age, hormone levels, and elucidated through multiple in vitro studies. However, it
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.2827