Page 8 - GPD-3-2
P. 8
Gene & Protein in Disease lncRNAs in trained immunity
nuclear RNAs, small nucleolar RNAs, and ribosomal lncRNA transcripts are reported, in contrast to the 19,940
RNAs. In contrast, regulatory RNAs, which govern gene protein-coding genes. 13
expression and cellular activities, include small ncRNAs The classification of lncRNAs into five distinct groups
such as miRNAs, siRNAs, piRNAs, and long ncRNAs is based on their chromosomal location and relationship
(lncRNAs). 3,6,7 The lncRNAs, a subset of endogenous to protein-coding genes. These include: (i) long intergenic
RNAs, have a length exceeding 200 nucleotides and do not ncRNA (lincRNA), transcribed between known protein-
possess the capacity to translate into proteins. Alternatively, coding genes; (ii) intronic lncRNA, transcribed within a
some lncRNAs may only encode very short peptides. 8-10 protein-coding gene’s introns; (iii) sense or pseudogene.
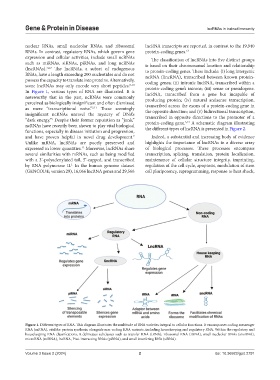
In Figure 1, various types of RNA are illustrated. It is lncRNA, transcribed from a gene but incapable of
noteworthy that in the past, ncRNAs were commonly producing protein; (iv) natural antisense transcription,
perceived as biologically insignificant and often dismissed transcribed across the exons of a protein-coding gene in
as mere “transcriptional noise.” These seemingly the opposite direction; and (v) bidirectional transcription,
5,11
insignificant ncRNAs unravel the mystery of DNA’s transcribed in opposite directions to the promoter of a
“dark energy.” Despite their former reputation as “junk,” protein-coding gene. A schematic diagram illustrating
5
5,14
ncRNAs have recently been shown to play vital biological
functions, especially in disease initiation and progression, the different types of lncRNA is presented in Figure 2.
7
and have proven helpful in novel drug development. Indeed, a substantial and increasing body of evidence
Unlike mRNA, lncRNAs are poorly preserved and highlights the importance of lncRNAs in a diverse array
expressed in lower quantities. Moreover, lncRNAs share of biological processes. These processes encompass
12
several similarities with mRNAs, such as being modified transcription, splicing, translation, protein localization,
with a 3’-polyadenylated tail, 5’-capped, and transcribed maintenance of cellular structure integrity, imprinting,
by RNA polymerase II. In the human genome dataset regulation of the cell cycle, apoptosis, modulation of stem
1
(GENCODE; version 29), 16,066 lncRNA genes and 29,566 cell pluripotency, reprogramming, response to heat shock,
Figure 1. Different types of RNA. This diagram illustrates the multitude of RNA varieties integral to cellular functions. It encompasses coding messenger
RNA (mRNA), vital for protein synthesis, alongside non-coding RNA variants, including housekeeping and regulatory RNA. Within the regulatory and
housekeeping RNA classifications, it delineates subclasses such as transfer RNA (tRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA), small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNA),
microRNA (miRNA), lncRNA, Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNA), and small interfering RNA (siRNA).
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 2 doi: 10.36922/gpd.2791