Page 9 - GPD-3-2
P. 9
Gene & Protein in Disease lncRNAs in trained immunity
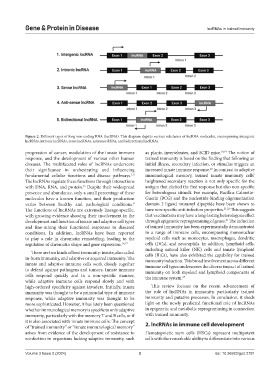
Figure 2. Different types of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA). This diagram depicts various subclasses of lncRNA molecules, encompassing intergenic
lncRNAs, intronic lncRNAs, sense lncRNAs, antisense RNAs, and bidirectional lncRNAs.
progression of cancer, modulation of the innate immune as plants, invertebrates, and SCID mice. 18,19 The notion of
response, and the development of various other human trained immunity is based on the finding that following an
diseases. The multifaceted roles of lncRNAs underscore initial illness, secondary infection, or stimulus triggers an
their significance in orchestrating and influencing increased innate immune response. In contrast to adaptive
20
fundamental cellular functions and disease pathways. immunological memory, trained innate immunity cells’
1,8
The lncRNAs regulate these functions through interactions heightened secondary reaction is not only specific for the
with DNA, RNA, and protein. Despite their widespread antigen that elicited the first response but also non-specific
15
presence and abundance, only a small percentage of these for heterologous stimuli. For example, Bacillus Calmette-
molecules have a known function, and their production Guerin (BCG) and the nucleotide-binding oligomerization
varies between healthy and pathological conditions. domain 2 ligand muramyl dipeptide have been shown to
8
The functions of lncRNAs are extremely lineage-specific, have non-specific anti-infection properties. 21,22 This suggests
with growing evidence showing their involvement in the that vaccinations may have a long-lasting heterologous effect
23
development and function of innate and adaptive cell types through epigenetic reprogramming of genes. The induction
and fine-tuning their functional responses to diseased of trained immunity has been experimentally demonstrated
conditions. In addition, lncRNAs have been reported in a range of immune cells, encompassing mononuclear
to play a role in chromatin remodeling, leading to the myeloid cells such as monocytes, macrophages, dendritic
regulation of chromatin shape and gene expression. 16,17 cells (DCs), and neutrophils. In addition, lymphoid cells,
including natural killer (NK) cells and innate lymphoid
There are two kinds of host immunity: innate, also called cells (ILCs), have also exhibited the capability for trained
in-born immunity, and adaptive or acquired immunity. The immunity induction. This broad involvement across different
innate and adaptive immune cells work closely together immune cell types underscores the diverse impact of trained
to defend against pathogens and tumors. Innate immune immunity on both myeloid and lymphoid components of
cells respond quickly and in a non-specific manner, the immune system. 24
while adaptive immune cells respond slowly and with
high-ordered specificity against invaders. Initially, innate This review focuses on the recent advancement of
immunity was thought to be a primordial type of immune the role of lncRNAs in immunity, particularly trained
response, while adaptive immunity was thought to be immunity and putative processes. In conclusion, it sheds
more sophisticated. However, it has lately been questioned light on the newly predicted functional role of lncRNAs
whether immunological memory is specific to only adaptive in epigenetic and metabolic reprogramming in connection
immunity, particularly with the memory T and B cells, or if with trained immunity.
it is also associated with innate immune cells. The concept
of “trained immunity” or “innate immunological memory” 2. lncRNAs in immune cell development
arises from evidence of the development of resistance to Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) represent multipotent
reinfection in organisms lacking adaptive immunity, such cells with the remarkable ability to differentiate into various
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 3 doi: 10.36922/gpd.2791