Page 11 - GPD-3-4
P. 11
Gene & Protein in Disease Human sirtuins (SIRT1-7) in cancer
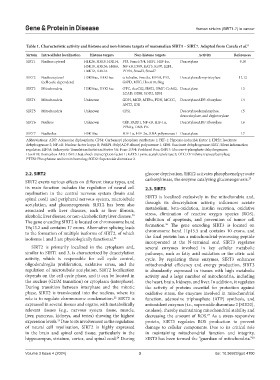
Table 1. Characteristic activity and histone and non-histone targets of mammalian SIRT1 – SIRT7. Adapted from Carafa et al. 8
Sirtuin Intracellular localization Histone targets Non-histone targets Activity References
SIRT1 Nucleus cytosol H1K26, H3K9, H3K14, P53, Foxo1/3/4, HSF1, HIF-1α, Deacetylase 9,10
H3K18, H3K56, H4K6, NF-κB, P300, KAT5, Ku70, E2F1,
H4K12, H4K16 PTEN, Smad3, Smad7
SIRT2 Nucleuscytosol H3K56ac, H4K16ac α-tubulin, Foxo3a, EIF5A, P53, Deacetylasedemyristoylase 11,12
(cell cycle dependent) G6PD, MYC, HoxA10, Slug
SIRT3 Mitochondria H3K56ac, H4K14ac OTC, AceCS2, IDH2, HMG-CoAS2, Deacetylase 13
LCAD, GDH, SOD2, SDH
SIRT4 Mitochondria Unknown GDH, MCD, MTPα, PDH, MCCC, DeacetylaseADP-ribosylase 14
ANT2, IDE
SIRT5 Mitochondria Unknown CPS1 Deacetylasedemalonylase, 15
desuccinylase, and deglutarylase
SIRT6 Nucleus Unknown CtlP, PARP1, NF-κB, HIF-1α, DeacetylaseADP-ribosylase 16
PPARγ, DNA-PK
SIRT7 Nucleolus H3K18ac HIF-1α, HIF-2α, RNA polymerase I Deacetylase 17
Abbreviations: ADP: Adenosine diphosphate; CPS1: Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1; HIF-1: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1; IDH2: Isocitrate
dehydrogenase 2; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; PARP1: Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1; SDH: Succinate dehydrogenase; SIRT: Silent information
regulator; EIF5A: Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 5A; Foxo 1/3/4: Forkhead Box; G6PD: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase;
HoxA10: Homeobox A10; HSF1: Heat shock transcription factor 1; KAT5: Lysine acetyltransferase 5; OTC: Ornithine transcarbamylase;
PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog; SOD2: Superoxide dismutase 2.
2.2. SIRT2 glucose deprivation, SIRT2 activates phosphoenolpyruvate
carboxykinase, the enzyme catalyzing gluconeogenesis. 25
SIRT2 exerts various effects on different tissue types, and
its main function includes the regulation of neural cell 2.3. SIRT3
myelination in the central nervous system (brain and
spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system, microtubule SIRT3 is localized exclusively in the mitochondria and,
acetylation, and gluconeogenesis. SIRT2 has been also through its deacetylation activity, influences acetate
associated with liver diseases, such as liver fibrosis, metabolism, beta-oxidation, insulin secretion, oxidative
alcoholic liver disease, or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. stress, elimination of reactive oxygen species (ROS),
20
The gene encoding SIRT2 is located on chromosome band inhibition of apoptosis, and prevention of tumor cell
26
19q13.2 and contains 17 exons. Alternative splicing leads formation. The gene encoding SIRT3 is located on
to the formation of multiple isoforms of SIRT2, of which chromosome band 11p15.5 and contains 10 exons, and
isoforms 1 and 2 are physiologically functional. 21 the final protein has a mitochondrial-processing peptide
incorporated at the N-terminal end. SIRT3 regulates
SIRT2 is primarily localized in the cytoplasm and, several enzymes involved in key cellular metabolic
similar to SIRT1 and 3, is characterized by deacetylation pathways, such as fatty acid oxidation or the citric acid
activity, which is responsible for cell cycle control, cycle. By regulating these enzymes, SIRT3 enhances
oligodendroglia proliferation, oxidative stress, and the mitochondrial efficiency and energy production. SIRT3
regulation of microtubule acetylation. SIRT2 localization is abundantly expressed in tissues with high metabolic
depends on the cell cycle phase, and it can be located in activity and a large number of mitochondria, including
the nucleus (G2/M transition) or cytoplasm (interphase). the heart, brain, kidneys, and liver. In addition, it regulates
During transition between interphase and the mitotic the activity of proteins essential for protection against
phase, SIRT2 is translocated into the nucleus, where its oxidative stress, the enzymes involved in mitochondrial
role is to regulate chromosome condensation. SIRT2 is function, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthesis, and
22
expressed in several tissues and organs, with metabolically antioxidant enzymes (i.e., superoxide dismutase 2 [SOD2],
relevant tissues (e.g., nervous system tissue, muscle, catalase), thereby maintaining mitochondrial stability and
liver, pancreas, kidneys, and testes) showing the highest decreasing the amount of ROS. As a stress-responsive
27
expression levels. Due to its involvement in the regulation protein, SIRT3 regulates ROS production to prevent
23
of neural cell myelination, SIRT2 is highly expressed damage to cellular components. Due to its critical role
in the brain and spinal cord tissue, particularly in the in maintaining mitochondrial function and integrity,
hippocampus, striatum, cortex, and spinal cord. During SIRT3 has been termed the “guardian of mitochondria.”
24
28
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 3 doi: 10.36922/gpd.4100