Page 15 - GPD-3-4
P. 15
Gene & Protein in Disease Human sirtuins (SIRT1-7) in cancer
in animal experiments on mouse embryonic fibroblasts cancer, SIRT7 has a dual character. Experiments on SIRT7-
in which SIRT6-knockdown cells showed increased knockout mice have shown increased susceptibility of
proliferation and tumorigenic characteristic. SIRT6 colorectal cancer cells. SIRT7 knockdown in tissue
100
113
knockdown in human hepatocellular cancer and non-small- samples and cell lines from patients with colorectal cancer
cell lung cancer cell lines promoted cell growth, whereas leads to significant inhibition of cell proliferation, cell
SIRT6 overexpression inhibited cell proliferation. 101,102 motility, and metastatic colony formation. In contrast,
In contrast, the oncogenic activity of SIRT6 has been ectopic SIRT7 expression promotes colony formation and
114
observed in various human cancer cell lines, including cell growth in vivo and in vitro. Tang et al. revealed a
ovarian cancer, prostate cancer, breast cancer, possible association between SIRT7 downregulation and
105
103
104
melanoma, and acute myeloid leukemia. 107 increased radiosensitivity triggering cell death in colorectal
106
cell lines. 115
3.7. SIRT7
4. Future prospects
Elevated SIRT7 expression has been observed in
metabolically active tissues (e.g., spleen and liver), Ongoing clinical trials and research will be crucial in
whereas low SIRT7 expression has been observed in non- elucidating the precise role of sirtuins in different types
proliferative tissues (e.g., brain and heart). Changes in SIRT7 of cancers and in developing safe, targeted therapies that
expression are seen across various tumor types, including leverage the dual role of sirtuins in cellular regulation.
hepatocellular cancer and bladder cancer, indicating The expression levels and activity patterns of SIRT1 –
108
109
its significant role in cellular processes that could influence 7 may provide valuable insights into cancer diagnosis
oncogenic transformation and tumor development. A and prognosis, as previous research has shown certain
110
conflicting effect of SIRT7 on cell proliferation has also dysregulation in different types of human cancers. 116,117
been reported. While SIRT7 downregulation in breast As shown in Figure 2, sirtuins may exert various plausible
cancer cell lines and patient tumor tissues promotes actions that interfere with multiple aspects of tumor biology.
metastatic character;, in ovarian cancer cell lines, it leads Future cancer therapies may aim to modulate sirtuin
111
to a significant reduction in cell growth and metastatic activity to restore normal cellular function, with a few
colony formation and increases apoptosis. In colorectal modulators already in clinical trials. Deus et al. reported
118
112
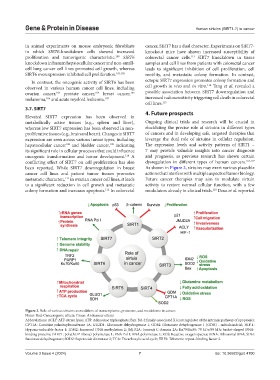
Figure 2. Role of various sirtuins as modifiers of transcriptome, proteome, and metablome in cancer.
Notes: Red: Cancerogenic effects; Green: Anticancer effects
Abbreviations: ACLY: ATP citrate lyase; ATP: Adenosine triphosphate; Bax: Bcl-2 family-associated X (core regulator of the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis);
CPT1A: Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A; GLUD1: Glutamate dehydrogenase 1; GDM: Glutamate dehydrogenase 1 (GDH) - mitochondrial; HIF-1:
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1; IDM2: Increased DNA methylation 2; JMJD2A: Jumonji C domain 2A; Ku70/Ku80: 70 kDa/80 kDa basket-shaped DNA-
binding proteins; PARP1: poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1; RNA Pol I: RNA polymerase 1; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; rRNA: Ribosomal RNA; SDH:
Succinate dehydrogenase; SOD2: Superoxide dismutase 2; TCA: Tricarboxylic acid cycle; TRF2: Telomeric repeat–binding factor 2.
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 7 doi: 10.36922/gpd.4100