Page 90 - GPD-4-2
P. 90
Gene & Protein in Disease Regulatory elements of ATP7B in WD
that provides valuable data on tissue- and cell-specific gene diagnosis for clinicians. We hypothesized that
expression and regulation across different individuals, hypomorphic alleles in key copper-metabolizing genes
developmental stages, and species. other than ATP7B may contribute to the WD phenotype,
potentially resulting in atypical or milder symptoms
2.5. Statistical analysis
compared to patients with two ATP7B mutated alleles.
The age of onset, serum ceruloplasmin levels, and 24-h Thus, we compared the clinical features and the age of
urinary copper levels were compared between the WD onset between three groups of patients: those with (i) no
patients with no coding mutation, a single mutated allele, ATP7B mutations, (ii) a single mutated ATP7B allele, and
and both mutations of ATP7B using an unpaired Student’s (iii) mutations in both alleles. However, no significant
t-test. P < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. differences were observed between the groups when
3. Results and discussions comparing the age of onset, serum ceruloplasmin
levels, and 24-h urinary copper levels using unpaired
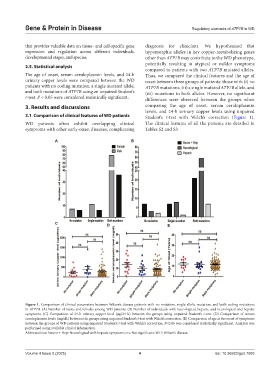
3.1. Comparison of clinical features of WD patients Student’s t-test with Welch’s correction (Figure 1).
WD patients often exhibit overlapping clinical The clinical features of all the patients are detailed in
symptoms with other early-onset diseases, complicating Tables S2 and S3.
A B
C D E
Figure 1. Comparison of clinical parameters between Wilson’s disease patients with no mutation, single allelic mutation, and both coding mutations
in ATP7B. (A) Number of males and females among WD patients. (B) Number of individuals with neurological, hepatic, and neurological and hepatic
symptoms. (C) Comparison of 24-h urinary copper level (µg/24 h) between the groups using unpaired Student’s t-test. (D) Comparison of serum
ceruloplasmin levels (mg/dL) between the groups using unpaired Student’s t-test with Welch’s correction. (E) Comparison of age at the onset of symptoms
between the groups of WD patients using unpaired Student’s t-test with Welch’s correction. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. Analysis was
performed using available clinical information.
Abbreviations: Neuro + Hep: Neurological with hepatic symptoms; ns: Not significant; WD: Wilson’s disease.
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 4 doi: 10.36922/gpd.7503