Page 91 - GPD-4-2
P. 91
Gene & Protein in Disease Regulatory elements of ATP7B in WD
3.2. Screening of cis-regulatory elements of ATP7B a single mutated allele in ATP7B (Figure 2A). These
among Indian WD patients single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) have minor
allele (T) frequencies of 0.378 and 0.395, respectively,
We selected three non-coding cis-regulatory elements for in the Bengali population in Bangladesh population,
the ATP7B gene from the list of eight previously identified according to the 1,000 Genome Browser. They are in
elements to screen in patients with either one or no linkage disequilibrium with an r LD value of 0.96, as per
20
2
mutations in ATP7B (Table 1). Two of these regulatory the HaploReg v4.1 database. The regulatory potential
39
elements exhibit a distal mode of gene regulation, located of these SNPs was assessed using RegulomeDB, which
37
13.12 kb and 3.6 kb upstream of the transcription start categorizes regulatory potential using a scoring scheme
site of ATP7B. The third regulatory element is in the 5’ ranging from 1 to 6, with lower values indicating higher
untranslated region of ATP7B. The distal regulators have regulatory potential. The rs2181891 (G/T) polymorphism
high DNase I hypersensitivity and H3K27Ac marks, shows a score of 1d, indicating its location within an
whereas the third element has low DNase I hypersensitivity eQTL, DNase I hypersensitive site, and transcription
and high H3K27Ac and H3K4me3 marks (Table 1). RNA factor binding region. Notably, its eQTL effect is
sequence data from the ENCODE database reveal the pronounced only in brain cerebellum tissue. Violin
expression of ATP7B in hepatic and neuronal tissues, as plots for the normalized genotype-specific expression
40
expected. The DNase I hypersensitivity at the selected profile of ATP7B show that the GG genotype presents the
regions correlates positively with ATP7B expression, as least expression while the TT genotype shows the highest
indicated by data from the Regulatory Element Database. expression (Figure 3). Nonetheless, the genotype-specific
Sequencing these three regions in the above-mentioned expression pattern was not distinct in other neuronal and
WD patients did not reveal any novel variants. However, hepatic tissues. The detailed information on the SNPs
we identified two heterozygous polymorphisms, identified among Indian WD patients with no mutation
rs2181891 (G/T) and rs747781 (C/T), in two WD patients and single allele coding mutation identified in ATP7B is
– one with no mutation in ATP7B and another containing depicted in Table 2.
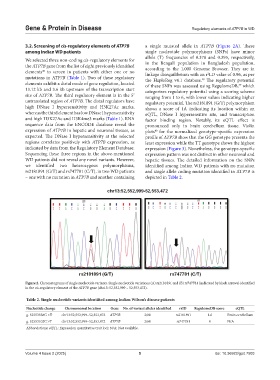
Figure 2. Chromatograms of single nucleotide variants. Single nucleotide variations (A) rs2181891 and (B) rs747781 (indicated by black arrows) identified
in the cis-regulatory element of the ATP7B gene (chr13: 52,552,999 – 52,553,472).
Table 2. Single nucleotide variants identified among Indian Wilson’s disease patients
Nucleotide change Chromosomal location Gene No. of variant alleles identified rsID RegulomeDB score eQTL
g. 52553358G >T chr13:52,552,999–52,553,472 ATP7B 2/60 rs2181891 1d Brain cerebellum
g. 52553102C >T chr13:52,552,999–52,553,472 ATP7B 2/60 rs747781 4 N/A
Abbreviations: eQTL: Expression quantitative trait loci; N/A: Not available.
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 5 doi: 10.36922/gpd.7503