Page 76 - GTM-1-1
P. 76
Global Translational Medicine ctDNA in management of patients with NSCLC
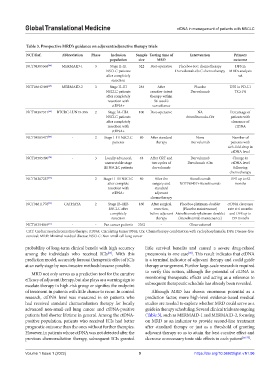
Table 3. Prospective MRD’s guidance on adjuvant/adjunctive therapy trials
NCT/Ref. Abbreviation Phase Inclusion Sample Testing time of Intervention Primary
population size MRD outcome
NCT04385368 [66] MERMAID-1 3 Stage II-III 322 Post-operative Placebo+SoC chemotherapy DFS in
NSCLC patients Durvalumab+SoC chemotherapy MRD+analysis
after completely set
resection
NCT04642469 [67] MERMAID-2 3 Stage II–III 284 After Placebo DFS in PD-L1
NSCLC patients curative-intent Durvalumab TC≥1%
after completely therapy within
resection with 96-week’s
ctDNA+ surveillance
NCT04367311 [68] BTCRC-LUN19-396 2 Stage IA–IIIA 100 Post-operative NA Percentage of
NSCLC patients Atezolizumab+Ctx patients with
after completely clearance of
resection with ctDNA
ctDNA+
NCT04585477 [69] - 2 Stage I–III NSCLC 80 After standard None Number of
patients therapy Durvalumab patients with
a≥3-fold drop in
ctDNA level
NCT04585490 [70] - 3 Locally advanced, 48 After CRT and Durvalumab Change in
unresectable stage two cycles of Duvalumab+Ctx ctDNA level
III NSCLC patients durvalumab following
chemotherapy
NCT04267237 [72] - 2 Stage II–III NSCLC 80 After the Atezolizumab DFS up to 62
after complete surgery and RO7198457+Atezolizumab months
resection with standard
ctDNA+ adjuvant
chemotherapy
NCT04611776 [73] CATHAYA 2 Stage IB–IIIB 160 After surgical Placebo+platinum-doublet ctDNA clearance
NSCLC after resection, (Placebo maintenance) rate at 6 months
completely before adjuvant Atezolizumab+platinum-doublet and DFS up to
resection therapy (Atezolizumab maintenance) 159 months
NCT04354064 [71] - - Pan cancer patients 3362 - Observational -
CRT: Cardiac resynchronization therapy; ctDNA: Circulating tumor DNA; Ctx: Chemotherapy combination with cyclophosphamide; DFS: Disease-free
survival; MRD: Minimal residual disease; NSCLC: Non-small cell lung cancer
probability of long-term clinical benefit with high accuracy little survival benefits and caused a severe drug-related
among the individuals who received ICIs . With this pneumonia in one case . This result indicates that ctDNA
[64]
[65]
prediction model, accurately forecast therapeutic effect of ICIs is a terminal indicator of adjuvant therapy and could guide
at an early stage by non-invasive methods became possible. therapy arrangement. Further large-scale research is required
MRD not only serves as a prediction tool for the curative to verify this notion, although the potential of ctDNA in
efficacy of adjuvant therapy, but also plays as a warning sign to monitoring therapeutic effects and acting as a reference to
escalate therapy in high-risk group or signifies the endpoint subsequent therapeutic schedule has already been revealed.
of treatment in patients with little chance to recur. In control Although MRD has shown enormous potential as a
research, ctDNA level was measured in 65 patients who prediction factor, more high-level evidence-based medical
had received standard chemoradiation therapy for locally studies are needed to explore whether MRD could serve as a
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and ctDNA-positive guide in therapy scheduling. Several clinical trials are ongoing
patients had shorter lifetime in general. Among the ctDNA- (Table 3), such as MERMAID-1 and MERMAID-2, focusing
positive population, patients who received ICIs had better on MRD as an indicator to provide second-line treatment
prognostic outcome than the ones without further therapies. after standard therapy or just as a threshold of granting
However, in patients whose ctDNA was not detected after the adjuvant therapy so as to attain the best curative effect and
previous chemoradiation therapy, subsequent ICIs granted decrease unnecessary toxic side effects in each patient [66-73] .
Volume 1 Issue 1 (2022) 9 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.v1i1.96