Page 74 - GTM-1-1
P. 74
Global Translational Medicine ctDNA in management of patients with NSCLC
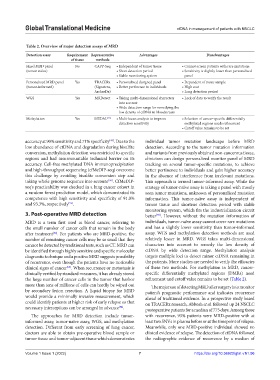
Table 2. Overview of major detection assays of MRD
Detection assay Requirement Representative Advantages Disadvantages
of tissue methods
Fixed MRD panel No CAPP-Seq • Independent of tumor tissue • Cannot screen patients with rare mutations
(tumor-naïve) • Short detection period • Sensitivity is slightly lower than personalized
• Stable monitoring system panel
Personalized MRD panel Yes TRACERx • Personalized designed panel • Dependent of tissue sample
(tumor-informed) (Signatera, • Better pertinence to individuals • High cost
ArcherDx) • Long detection period
WGS Yes MRDetect • Taking multi‑dimensional characters • Lack of data to verify the result
into account
• Wide detection range for remedying the
low density of ctDNA in bloodstream
Methylation Yes MEDAL [77] • Multi‑locus analysis to improve • Selection of cancer‑specific differentially
detection sensitivity methylated regions needs refinement
• Cutoff value remains to be set
accuracy at 90% sensitivity and 71% specificity . Due to the individual tumor mutation landscape before MRD
[49]
low abundance of ctDNA and degradation during bisulfite detection. According to the tumor mutation information
conversion, methylation detection was restricted to specific and variants from previously obtained non-cancerous tissue,
regions and had insurmountable technical barrier on its clinicians can design personalized monitor panel of MRD
accuracy. Cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation tracking on several tumor-specific mutations, to achieve
and high-throughput sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq) overcome better pertinence to individuals and gain higher accuracy
this challenge by avoiding bisulfite conversion step and in the absence of interference from irrelevant mutations.
taking whole genome sequence into account . CfMeDIP- This approach is termed tumor-informed assay. While the
[50]
seq’s practicability was checked in a lung cancer cohort in strategy of tumor-naïve assay is taking a panel with mostly
a random forest prediction model, which demonstrated its seen tumor mutations, unknown of personalized mutation
competence with high sensitivity and specificity of 91.0% information. This tumor-naïve assay is independent of
and 93.3%, respectively . tumor tissue and shortens detection period with stable
[51]
monitoring system, which fits the industrialization circuit
3. Post-operative MRD detection better . However, without the mutation information of
[55]
MRD is a term first used in blood cancer, referring to individuals, tumor-naïve assay cannot cover rare mutations
the small number of cancer cells that remain in the body and has a slightly lower sensitivity than tumor-informed
after treatment . For patients who are MRD-positive, the assay. WGS and methylation detection methods are used
[52]
number of remaining cancer cells may be so small that they relatively lesser in MRD. WGS takes multi-dimensional
cannot be detected by traditional tests, such as CT. MRD can characters into account to remedy the low density of
be identified through highly sensitive and specific molecular ctDNA by wide detection range. Methylation analysis
diagnostic technique and a positive MRD suggests possibility targets multiple loci to detect minor ctDNA remaining in
of recurrence, even though the patients have no noticeable the patients. More studies are needed to verify the efficacies
clinical signs of cancer . When recurrence or metastasis is of these two methods. For methylation in MRD, cancer-
[53]
clinically verified by standard measures, it has already stored specific differentially methylated regions (DMRs) need
the large number of cancer cells in the tumor that harbor refinement and cutoff value remains to be set (Table 2).
more than tens of millions of cells can hardly be wiped out The major use of detecting MRD after surgery is to monitor
by secondary lesion resection. A liquid biopsy for MRD patient’s prognostic performance and indicates recurrence
would provide a minimally invasive measurement, which ahead of traditional evidence. In a prospective study based
could identify patients at higher risk of early relapse so that on TRACERx research, Abbosh et al. followed up 24 NSCLC
necessary interceptions can be arranged in advance . postoperative patients for a median of 775 days. Among those
[54]
The approaches for MRD detection include tumor- with recurrence, 93% patients were MRD-positive with at
informed assay, tumor-naïve assay, WGS, and methylation least two SNVs in plasma before or at the timepoint of relapse.
detection. Different from early screening of lung cancer, Meanwhile, only one MRD-positive individual showed no
doctors are able to obtain pre-operative blood sample or clinical evidence of relapse. The detection of ctDNA followed
tumor tissue and tumor-adjacent tissue which demonstrates the radiographic evidence of recurrence by a median of
Volume 1 Issue 1 (2022) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.v1i1.96