Page 55 - GTM-2-4
P. 55
Global Translational Medicine Epigenetics on cardiovascular diseases
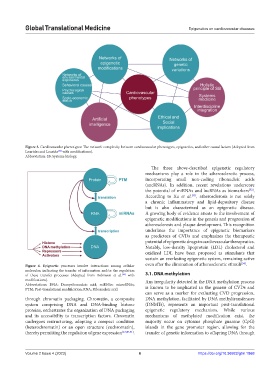
Figure 3. Cardiovascular phenotypes: The network complexity between cardiovascular phenotypes, epigenetics, and other causal factors (Adopted from
[32]
Louridas and Lourida with modifications).
Abbreviation: SB: Systems biology.
The three above-described epigenetic regulatory
mechanisms play a role in the atherosclerotic process,
incorporating small non-coding ribonucleic acids
(sncRNAs). In addition, recent revelations underscore
the potential of miRNAs and lncRNAs as biomarkers .
[52]
According to Xu et al. , atherosclerosis is not solely
[53]
a chronic inflammatory and lipid-depository disease
but is also characterized as an epigenetic disease.
A growing body of evidence attests to the involvement of
epigenetic modifications in the genesis and progression of
atherosclerosis and plaque development. This recognition
underlines the importance of epigenetic biomarkers
as predictors of CVDs and emphasizes the therapeutic
potential of epigenetic drugs in cardiovascular therapeutics.
Notably, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and
oxidized LDL have been proposed as stimulants that
sustain an everlasting epigenetic system, remaining active
[54]
Figure 4. Epigenetic processes involve interactions among cellular even after the elimination of atherosclerotic stimuli .
molecules, indicating the transfer of information and/or the regulation
of these transfer processes (Adopted from Robinson et al. with 3.1. DNA methylation
[38]
modifications). Any irregularity detected in the DNA methylation process
Abbreviations: DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid; miRNAs: microRNAs;
PTM: Post-translational modification; RNA: Ribonucleic acid. is known to be implicated in the genesis of CVDs and
can serve as a marker for evaluating CVD progression.
through chromatin packaging. Chromatin, a composite DNA methylation, facilitated by DNA methyltransferases
system comprising DNA and DNA-binding histone (DNMTs), represents an important post-translational
proteins, orchestrates the organization of DNA packaging epigenetic regulatory mechanism. While various
and its accessibility to transcription factors. Chromatin mechanisms of methylated modification exist, the
undergoes restructuring, adopting a compact condition majority occur on cytosine phosphate guanine (CpG)
(heterochromatin) or an open structure (euchromatin), islands in the gene promoter region, allowing for the
thereby permitting the regulation of gene expression [17,49-51] . transfer of genetic information to offspring DNA through
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.1868