Page 11 - GTM-3-1
P. 11
Global Translational Medicine Role of HTS in cancer therapeutics
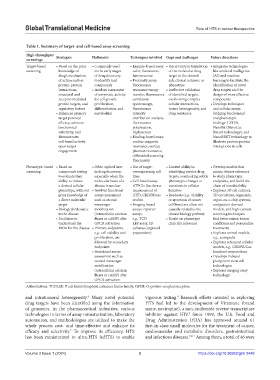
Table 1. Summary of target‑ and cell‑based assay screening
High‑throughput Strategies Hallmarks Techniques involved Gaps and challenges Future directions
screenings
Target-based • Based on the prior • Commonly used • Enzyme‑based assay: • Uncertainty in translation • Integrates technologies
screening knowledge of in the early stages color, fluorescent, of the molecular drug like artificial intelligence
drug’s mechanism of drug discovery luminescence target to the desired (AI) and machine
of action such as to identify lead • Proximity assay: safe clinical outcome or learning to facilitate the
protein-protein compounds fluorescence phenotype identification of novel
interactions, • Involves assessment resonance energy • Ineffective validation drug targets and the
structural and of enzymatic activity transfer, fluorescence of identified targets, design of more effective
receptor-mediated for cell growth, correlation overlooking complex compounds
protein targets, and proliferation, spectroscopy, cellular interactions, • Develops techniques
regulatory factors differentiation, and fluorescence tumor heterogeneity, and and cellular assays
• Enhances primary metabolism intensity drug resistance bridging biochemical
target potency/ distribution analysis, and phenotypic
efficacy, achieves fluorescence findings: CETSA,
biochemical polarization, NanoBit (NanoLuc
selectivity, and Alphascreen Binary technology), and
demonstrates • Binding‑based assay: NanoBRET technology to
cell-based activity nuclear magnetic illustrate protein-protein
upon target resonance, surface interactions in cells
engagement plasmon resonance,
differential scanning
fluorimetry
Phenotype- based • Based on • Often applied later • Use of target‑ • Limited ability in • Develop models that
screening compounds testing in drug discovery, overexpressing cell identifying precise drug mimic disease relevance
to evaluate their especially when the lines targets, overlooking subtle to study phenotypic
ability to induce molecular basis of a • Cell‑based assay: phenotypic changes or endpoints, and build the
a desired cellular disease is unclear ATPGlo (luciferase variations in cellular chain of translatability
phenotype, with-out • Involves functional measurement of behavior • Explores 3D cell cultures,
prior knowledge of assays assessment ATP), CRISPR/cas • Readouts (e.g., viability 3D cocultures, organoids,
a direct molecular such as second studies or apoptosis of cancer organ-on-a-chip systems,
target messenger • Imaging‑based cell lines) are often not and patient-derived
• Biological relevance mobilization assays: reporter causally related to the models, and high-content
to the disease (intracellular calcium assays, disease biology pathway screening techniques
• Facilitates to fluxes or cAMP) after e.g., TCF/ • Doubt on phenotype that better mimic tumor
understand the GPCR activation LEF assay, 3D clinically relevance conditions and personalize
MOA for the disease • Primary endpoints, cultures (organoid treatments
e.g., cell viability and preparation) • Explores animal models,
proliferation, are e.g., xenografts
followed by secondary • Explores advanced cellular
endpoints models, e.g., CRISPR/Cas
• Functional assays knockout preparations
assessment such as • Develops induced
second messenger pluripotent stem cell
mobilization technologies
(intracellular calcium • Explores imaging assay
fluxes or cAMP) after technology
GPCR activation
Abbreviations: TCF/LEF: T cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor family; GPCR: G‑protein‑coupled receptors.
and intratumoral heterogeneity. Many novel potential vigorous testing. Research efforts invested in exploring
8
6
drug targets have been identified using the information HTS had led to the development of Viramune (brand
of genomics. In the pharmaceutical industries, various name, nevirapine), a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase
technologies in terms of assay miniaturization, laboratory inhibitor against HIV. Since 1999, the U.S. Food and
9
automation, and methodologies are utilized to make the Drug Administration (FDA) has approved around 61
whole process cost- and time-effective and enhance its first-in-class small molecules for the treatment of cancer,
efficacy and selectivity. To improve its efficiency, HTS cardiovascular and metabolic disorders, gastrointestinal
7
has been miniaturized to ultra-HTS (uHTS) to enable and infectious diseases. 10,11 Among them, a total of 46 were
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.2448