Page 13 - GTM-3-1
P. 13
Global Translational Medicine Role of HTS in cancer therapeutics
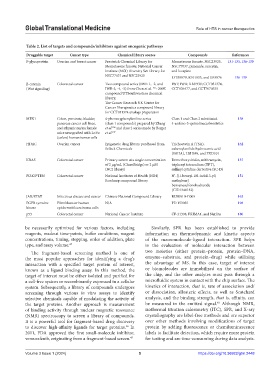
Table 2. List of targets and compounds/inhibitors against oncogenic pathways
Druggable target Cancer type Chemical library source Compounds References
P-glycoprotein Ovarian and breast cancer Prestwick Chemical Library for Mometasone furoate, NSC23925, 131-133, 136-139
Mometasone furoate; National Cancer NSC77037, pimozide, acacetin,
Institute (NCI) Diversity Set Library for and loxapine
NSC77037 and NSC23925 LY335979, R101933, and XR9576 136-139
β-catenin Colorectal cancer Two compound series (IWR-1, -2, and IWP, IWR; XAV939; CCT031374,
(Wnt signaling) IWR‑3, ‑4, ‑5) from Chen et al. ~200K CCT036477, and CCT7070535
195
compound UTSouthwestern chemical
library;
The Cancer Research UK Centre for
Cancer Therapeutics compound library
for CCT031374 analogs preparation
MEK1 Colon, prostrate, bladder, 4-phenoxyphenylaniline series Class 1 and Class 2 substituted 158
pancreas cancer cell lines, (class 1 compounds) prepared by Zhang 4-anilino-3-quinolinecarbonitriles
196
and athymic nu/nu female et al. and class 2 series made by Berger
mice xenografted with LoVo et al. 197
(colon) human tumor cells
HDAC Ovarian cancer Epigenetic drug library purchased from Trichostatin A (TSA), 162
Selleck Chemicals suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid
(SAHA), LBH589, and PXD101
KRAS Colorectal cancer Primary screen at a single concentration Demethoxyviridin, mithramycin, 157
of 2 μg/mL (ChemBridge) or 2 μM triphenyl tetrazolium (TPT),
(NCI library) sulfinyl cytidine derivative (SC‑D)
PI3K/PTEN Colorectal cancer National Institutes of Health (NIH) N’-[(1-benzyl-1H-indol-3-yl) 151
Roadmap compound library methylene]
benzenesulfonohydrazide
(CID1340132)
JAK/STAT Infectious disease and cancer Chinese National Compound Library RUS0910-G009 163
EGFR tyrosine Fibroblasts or human N/A PD 153035 198
kinase epidermoid carcinoma cells
p53 Colorectal cancer National Cancer Institute CP‑31398, PRIMA1, and Nutlins 180
be necessarily optimized for various factors, including Similarly, SPR has been established to provide
reagents, readout time-points, buffer conditions, reagent information on thermodynamic and kinetic aspects
concentrations, timing, stopping, order of addition, plate of the macromolecule-ligand interaction. SPR helps
type, and assay volume. 45 in the evaluation of molecular interaction between
The fragment-based screening method is one of two moieties (either protein–protein, protein–DNA,
the most popular approaches for identifying a drug’s enzyme–substrate, and protein–drug) while utilizing
interaction with a specified target protein of interest, the advantage of MS. In this case, target of interest
known as a ligand binding assay. In this method, the or biomolecules are immobilized on the surface of
target of interest must be either isolated and purified for the chip, and the other analytes must pass through a
a cell-free system or recombinantly expressed in a cellular microfluidic system in contact with the chip surface. The
system. Subsequently, a library of compounds undergoes kinetics of interaction, that is, rate of association and/
screening through various in vitro assays to identify or dissociation, allosteric effects, as well as Scatchard
selective chemicals capable of modulating the activity of analysis, and the binding strength, that is, affinity, can
48
the target proteins. Another approach is measurement be measured in the emitted signal. Although NMR,
of binding activity through nuclear magnetic resonance isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC), SPR, and X‑ray
(NMR) spectroscopy to screen a library of compounds. crystallography are label-free methods and are superior
It is a powerful tool for fragment-based drug discovery over other methods involving modifications of target
to discover high-affinity ligands for target proteins. In protein by adding fluorescence or chemiluminescence
46
2011, FDA approved the first small-molecule inhibitor, labels to facilitate detection, which require more protein
vemurafenib, originating from a fragment-based screen. 47 for testing and are time-consuming during data analysis.
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.2448