Page 130 - IJB-10-3
P. 130
International Journal of Bioprinting New challenges in liver tissue engineering
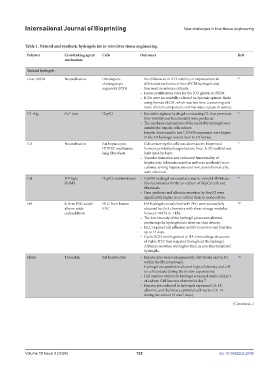
Table 1. Natural and synthetic hydrogels for in vitro liver tissue engineering
Polymer Crosslinking agent/ Cells Outcomes Refs
mechanism
Natural hydrogels
Liver dECM Neutralization Intrahepatic – No differences in ICO viability or improvement in 94
cholangiocyte differentiation between liver dECM hydrogels and
organoids (ICO) basement membrane extracts.
– Lower proliferation rates for the ICO grown in dECM.
– ICOs were successfully cultured in dynamic spinner flasks
using human dECM, which was less time-consuming and
more efficient compared to normal static culture in domes.
GL-Alg Ca ions HepG2 – Injectable alginate hydrogels containing GL that promoted 87
2+
liver viability and functionality were produced.
– The mechanical properties of the injectable hydrogel were
suitable for hepatic cells culture.
– Hepatic functionality and CYP450 expression were higher
in the 3D hydrogel system than in 2D format.
Col Neutralization Rat hepatocytes, – Col containing the cells was alternatively bioprinted 97
HUVEC and human between printed polycaprolactone lines. A 3D scaffold was
lung fibroblasts built layer-by-layer.
– Vascular formation and enhanced functionality of
hepatocytes (albumin secretion and urea synthesis) in co-
cultures, among hepatocytes and non-parenchymal cells,
were observed.
Gel UV-light HepG2 and fibroblasts – GelMA hydrogel was used as a matrix to build 3D lobule- 98
GelMA like microtissues for the co-culture of HepG2 cells and
fibroblasts.
– Urea synthesis and albumin secretion by HepG2 were
significantly higher in co-culture than in monoculture.
HA 8-Arm PEG-azide/ HLC from human – HA hydrogels crosslinked with PEG were successfully 100
alkyne-azide iPSC obtained by click chemistry with shear storage modulus
cycloaddition between 100 Pa to 1 kPa.
– The low viscosity of the hydrogel precursors allowed
producing the hydrogels into liver-on-chip devices.
– HLC required cell adhesion motifs to survive and function
up to 13 days.
– Cyclic RGD motifs grafted to HA formed large structures
of viable HLC that migrated throughout the hydrogel.
Albumin secretion was higher than in non-functionalized
hydrogels.
Fibrin Thrombin Rat hepatocytes – Hepatocytes were homogeneously distributed and in 3D 116
within the fibrin hydrogel.
– Hydrogel encapsulation allowed high cell density and cell-
to-cell contacts during the in vitro experiments.
– Cell number within the hydrogel remained stable till day 3
of culture. Cell loss was observed at day 7.
– Hepatocytes cultured in hydrogels expressed CK-18,
albumin, and the biliary epithelial cell marker CK-19
during the culture (3 and 7 days).
(Continued...)
Volume 10 Issue 3 (2024) 122 doi: 10.36922/ijb.2706