Page 127 - IJB-10-3
P. 127
International Journal of Bioprinting New challenges in liver tissue engineering
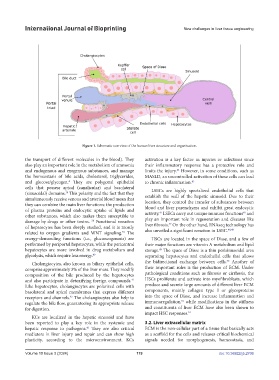
Figure 1. Schematic overview of the human liver structure and organization.
the transport of different molecules in the blood). They activation is a key factor in injuries or infections since
also play an important role in the metabolism of ammonia their inflammatory response has a protective role and
and endogenous and exogenous substances, and manage limits the injury. However, in some conditions, such as
44
the homeostasis of bile acids, cholesterol, triglycerides, MASLD, an uncontrolled activation of these cells can lead
and glucose/glycogen. They are polygonal epithelial to chronic inflammation. 43
4
cells that possess apical (canalicular) and basolateral LSECs are highly specialized endothelial cells that
(sinusoidal) domains. This polarity and the fact that they establish the wall of the hepatic sinusoid. Due to their
38
simultaneously receive venous and arterial blood mean that
they can combine the main liver functions: the production location, they control the transfer of substances between
of plasma proteins and endocytic uptake of lipids and blood and liver parenchyma and exhibit great endocytic
46
45
other substances, which also makes them susceptible to activity. LSECs carry out unique immune functions and
damage by drugs or other toxins. Functional zonation play an important role in regeneration and diseases like
38
47
of hepatocytes has been deeply studied, and it is mostly liver fibrosis. On the other hand, RNAseq technology has
40,48
related to oxygen gradients and WNT signaling. The also unveiled a significant zonation in LSEC.
39
energy-demanding functions (i.e., gluconeogenesis) are HSCs are located in the space of Disse, and a few of
performed by periportal hepatocytes, while the pericentral their major functions are vitamin A metabolism and lipid
hepatocytes are more involved in drug metabolism and storage. The space of Disse is a thin perisinusoidal area
49
glycolysis, which require less energy. 40 separating hepatocytes and endothelial cells that allows
50
Cholangiocytes, also known as biliary epithelial cells, the bidirectional exchange between cells. Another of
comprise approximately 3% of the liver mass. They modify their important roles is the production of ECM. Under
composition of the bile produced by the hepatocytes pathological conditions such as fibrosis or cirrhosis, the
and also participate in detoxifying foreign compounds. HSCs proliferate and activate into myofibroblasts, which
41
Like hepatocytes, cholangiocytes are polarized cells with produce and secrete large amounts of different liver ECM
basolateral and apical membranes that express different components, mainly collagen type I or glycoproteins
receptors and channels. The cholangiocytes also help to into the space of Disse, and increase inflammation and
42
51
regulate the bile flow, guaranteeing its appropriate release immunoregulation, while modifications in the stiffness
for digestion. and constituents of liver ECM have also been shown to
impact HSC responses. 51
KCs are localized in the hepatic sinusoid and have
been reported to play a key role in the systemic and 3.2. Liver extracellular matrix
hepatic response to pathogens. They are also critical ECM is the non-cellular part of a tissue that basically acts
43
mediators in liver injury and repair and can show high as a scaffold for the cells and releases critical biochemical
plasticity, according to the microenvironment. KCs signals needed for morphogenesis, homeostasis, and
Volume 10 Issue 3 (2024) 119 doi: 10.36922/ijb.2706