Page 6 - IJB-6-2
P. 6
Electrically conducting hydrogels for health care: Concept, fabrication methods, and applications
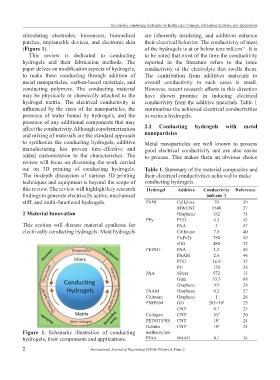
stimulating electrodes, biosensors, biomedical are inherently insulating, and additives enhance
patches, implantable devices, and electronic skin their electrical behavior. The conductivity of most
(Figure 1). of the hydrogels is at or below tens mS.cm . It is
−1
This review is dedicated to conducting to be noted that most of the time the conductivity
hydrogels and their fabrication methods. The reported in the literature refers to the ionic
paper delves on modification aspects of hydrogels, conductivity of the electrolyte that swells them.
to make them conducting through addition of The contribution from additives materials to
metal nanoparticles, carbon-based materials, and overall conductivity in such cases is small.
conducting polymers. The conducting material However, recent research efforts in this direction
may be physically or chemically attached to the have shown promise in inducing electrical
hydrogel matrix. The electrical conductivity is conductivity from the additive materials. Table 1
influenced by the sizes of the nanoparticles, the summarizes the achieved electrical conductivities
presence of water bound by hydrogels, and the in various hydrogels.
presence of any additional components that may
affect the conductivity. Although copolymerization 2.1 Conducting hydrogels with metal
and mixing of materials are the standard approach nanoparticles
to synthesize the conducting hydrogels, additive Metal nanoparticles are well known to possess
manufacturing has proven time-effective and good electrical conductivity and are also easier
added customization to the characteristics. The to process. This makes them an obvious choice
review will focus on discussing the work carried
out on 3D printing of conducting hydrogels. Table 1. Summary of the material composites and
The in-depth discussion of various 3D printing their electrical conductivities achieved to make
techniques and equipment is beyond the scope of conducting hydrogels.
this review. The review will highlight key research Hydrogel Additive Conductivity Reference
findings to generate electrically active, mechanical (mS.cm )
−1
stiff, and multi-functional hydrogels. PANI Cellulose 70 39
MWCNT 1540 27
2 Material Innovation Graphene 182 31
PPy PEG 4.3 43
This section will discuss material synthesis for PAA 5 47
electrically conducting hydrogels. Most hydrogels Cellulose 7.8 40
CuPcTs 780 49
rGO 480 32
PEDOT PAA 1.2 48
PAAM 2.6 46
PEG 16.9 37
PU 120 38
PAA Silver 572 13
Gum 33.5 88
Graphene 10 -3 28
PAAM Graphene 0.2 27
Chitosan Graphene 1 26
PNIPAM GO 285×10 4 25
CNT 0.7 25
Collagen CNT 10 -7 20
PEDOT:PSS CNT 10 5 24
Gelatin CNT 10 2 21
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of conducting methacrylate
hydrogels, their components and applications. PTAA MAAG 0.1 36
2 International Journal of Bioprinting (2020)–Volume 6, Issue 2