Page 11 - IJB-6-2
P. 11
Agarwala
A wherein either a material precursor is illuminated
by light or a pattern is projected [67,69] . Curing of
the material takes places in selected regions where
the light hits it. In most printers, the printhead
and platform move in X-Y directions relative to
each other. However, here a Z-displacement of
the precursor reservoir is performed to fabricate
a 3D shape. Detailed discussion on operation and
methodology of these techniques is beyond the
scope of this review. Hydrogel to be processed
B through the printer needs to be converted into an ink
format. Ink development is considered one of the
most important aspects of 3D printing. Hydrogel
inks need to have the right rheological properties
to fulfill the physical and mechanical needs of the
orienting process. Ink formulation, properties, and
optimization are a widely researched [70-72] area and
will not be discussed in this paper.
Sayyar et al. used extrusion based bioplotting
system to print graphene-chitosan composite
C biocompatible scaffolds. Addition of 3% of
graphene in the composite resulted in 200%
enhancement of mechanical strength . They
[28]
further developed a new UV-crosslinkable
conducting hydrogel based on the same
materials . Functionalized chitosan served as the
[73]
host polymer and chemically converted graphene
as the filler. The incorporation of graphene into
chitosan resulted in cytocompatible matrix with
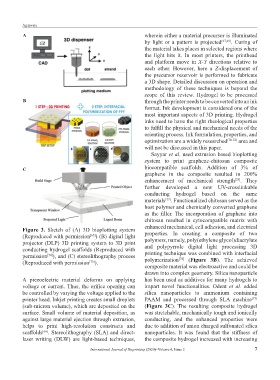
Figure 3. Sketch of (A) 3D bioplotting system enhanced mechanical, cell adhesion, and electrical
(Reproduced with permission ) (B) digital light properties. In creating a composite of two
[65]
projector (DLP) 3D printing system to 3D print polymers, namely, poly(ethylene glycol)diacrylate
conducting hydrogel scaffolds (Reproduced with and polypyrrole digital light processing 3D
permission ), and (C) stereolithography process printing technique was combined with interfacial
[74]
[74]
(Reproduced with permission ). polymerization (Figure 3B). The achieved
[75]
composite material was electroactive and could be
drawn into complex geometry. Silica nanoparticle
A piezoelectric material deforms on applying has been used as additives for many hydrogels to
voltage or current. Thus, the orifice opening can impart novel functionalities. Odent et al. added
be controlled by varying the voltage applied to the silica nanoparticles to ammonium containing
printer head. Inkjet printing creates small droplets PAAM and processed through SLA machine
[75]
(sub-micron volume), which are deposited on the (Figure 3C). The resulting composite hydrogel
surface. Small volume of material deposition, as was stretchable, mechanically tough and ionically
against large material ejection through extrusion, conducting, and the enhanced properties were
helps to print high-resolution constructs and due to addition of anion charged sulfonated silica
scaffolds . Stereolithography (SLA) and direct- nanoparticles. It was found that the stiffness of
[66]
laser writing (DLW) are light-based techniques, the composite hydrogel increased with increasing
International Journal of Bioprinting (2020)–Volume 6, Issue 2 7