Page 83 - IJB-6-3
P. 83
Yusupov, et al.
For transferred objects, it is important to select
the physicochemical characteristics of the hydrogel
medium: The viscosity, surface tension, and the
nature (polymer or inorganic). Furthermore,
the presence of the additives (growth factors,
proteins, etc.) in the gel helps to create the most
favorable conditions for the metabolism of the
transferred objects. In some cases, an important
factor is also the geometric arrangement of
droplets on the acceptor surface, which provides,
in particular, the optimal overlap and droplet
spacing of individual non-merging drops [37,38] .
At present, a number of laser systems have
been described in the scientific literature where
LIFT printing is feasible [24,31] . However, it is worth
noting that the selection of optimal parameters
for a specific combination of laser-hydrogel
microobjects actually represents a separate study.
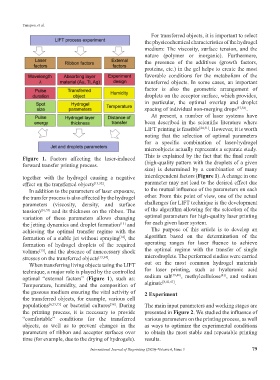
Figure 1. Factors affecting the laser-induced This is explained by the fact that the final result
forward transfer printing process. (high-quality pattern with the droplets of a given
size) is determined by a combination of many
together with the hydrogel causing a negative interdependent factors (Figure 1). A change in one
effect on the transferred objects [13,32] . parameter may not lead to the desired effect due
In addition to the parameters of laser exposure, to the mutual influence of the parameters on each
the transfer process is also affected by the hydrogel other. From this point of view, one of the actual
parameters (viscosity, density, and surface challenges for LIFT technique is the development
tension) [16,33] and its thickness on the ribbon. The of the algorithm allowing for the selection of the
variation of these parameters allows changing optimal parameters for high-quality laser printing
the jetting dynamics and droplet formation and for each given laser system.
[15]
achieving the optimal transfer regime with the The purpose of this article is to develop an
formation of a stable jet without spraying , the algorithm based on the determination of the
[14]
formation of hydrogel droplets of the required operating ranges for laser fluence to achieve
volume , and the absence of unnecessary shock the optimal regime with the transfer of single
[15]
stresses on the transferred objects [13,34] . microdroplets. The performed studies were carried
When transferring living objects using the LIFT out on the most common hydrogel materials
technique, a major role is played by the controlled for laser printing, such as hyaluronic acid
[41]
optimal “external factors” (Figure 1), such as: sodium salt [39,40] , methylcellulose , and sodium
Temperature, humidity, and the composition of alginate [8,42,43] .
the gaseous medium ensuring the vital activity of 2 Experiment
the transferred objects, for example, various cell
populations [6,23,35] or bacterial cultures . During The main input parameters and working stages are
[36]
the printing process, it is necessary to provide presented in Figure 2. We studied the influence of
“comfortable” conditions for the transferred various parameters on the printing process, as well
objects, as well as to prevent changes in the as ways to optimize the experimental conditions
parameters of ribbon and acceptor surfaces over to obtain the most stable and repeatable printing
time (for example, due to the drying of hydrogels). results.
International Journal of Bioprinting (2020)–Volume 6, Issue 3 79