Page 9 - IJB-7-3
P. 9
Liu, et al.
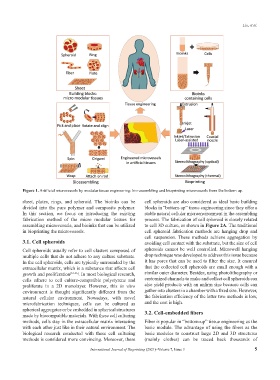
Figure 1. Artificial microvessels by modular tissue engineering: bio-assembling and bioprinting microvessels from the bottom up.
sheet, plates, rings, and spheroid. The bioinks can be cell spheroids are also considered as ideal basic building
divided into the pure polymer and composite polymer. blocks in “bottom-up” tissue engineering since they offer a
In this section, we focus on introducing the existing stable natural cellular microenvironment in the assembling
fabrication method of the micro modular tissues for process. The fabrication of cell spheroid is closely related
assembling microvessels, and bioinks that can be utilized to cell 3D culture, as shown in Figure 2A. The traditional
in bioprinting the microvessels. cell spheroid fabrication methods are hanging drop and
cell suspension. These methods achieve aggregation by
3.1. Cell spheroids avoiding cell contact with the substrate, but the size of cell
Cell spheroids usually refer to cell clusters composed of spheroids cannot be well controlled. Microwell hanging
multiple cells that do not adhere to any culture substrate. drop technique was developed to address this issue because
In the cell spheroids, cells are typically surrounded by the it has pores that can be used to filter the size. It ensured
extracellular matrix, which is a substance that affects cell that the collected cell spheroids are small enough with a
growth and proliferation [34-36] . In most biological research, similar outer diameter. Besides, using photolithography or
cells adhere to cell culture-compatible polystyrene and customized channels to make and collect cell spheroids can
proliferate in a 2D monolayer. However, this in vitro also yield products with an unfirm size because cells can
environment is thought significantly different from the gather into clusters in a chamber with a fixed size. However,
natural cellular environment. Nowadays, with novel the fabrication efficiency of the latter two methods is low,
microfabrication techniques, cells can be cultured as and the cost is high.
spherical aggregates or be embedded in spherical structures 3.2. Cell-embedded fibers
made by biocompatible materials. With these cell culturing
methods, cells stay in the extracellular matrix interacting Fiber is popular in “bottom-up” tissue engineering as the
with each other just like in their natural environment. The basic module. The advantage of using the fibers as the
biological research conducted with these cell culturing basic modules to construct large 2D and 3D structures
methods is considered more convincing. Moreover, these (mainly clothes) can be traced back thousands of
International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 3 5