Page 10 - IJB-7-3
P. 10
Bottom-Up Microvessel Engineering
A B C
D
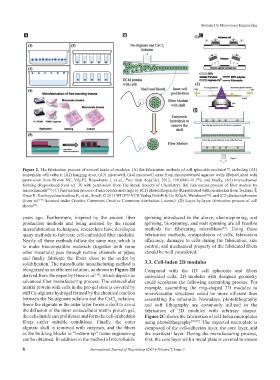
Figure 2. The fabrication process of several kinds of modules. (A) Six fabrication methods of cell spheroids modules , including (A1)
[34]
suspension cell culture, (A2) hanging drop, (A3) microwell, (A4) microwell array from micropatterned agarose wells (Republished with
permission from Rivron NC, Vrij EJ, Rouwkema J, et al., Proc Natl Acad Sci, 2012, 109:6886–91. ), and finally, (A5) microchannel
[35]
forming (Reproduced from ref. 36 with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry). (B) Fabrication process of fiber module by
microchannels . (C) Fabrication process of microplates and rings by (C1) photolithography (Republished with permission from Teshima T,
[30]
Onoe H, Kuribayashiashiashias K, et al., Small, © 2013 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim ). and (C2) dielectrophoresis
[38]
(from ref. licensed under Creative Commons Creative Commons Attribution License). (D) Layer-by-layer fabrication process of cell
[39]
sheets .
[44]
years ago. Furthermore, inspired by the ancient fiber spinning introduced in the above, electrospinning, wet
production methods and being assisted by the recent spinning, biospinning, and melt spinning are all feasible
microfabrication techniques, researchers have developed methods for fabricating microfibers . Using these
[37]
many methods to fabricate cell-embedded fiber modules. fabrication methods, encapsulation of cells, fabrication
Nearly all these methods follow the same way, which is efficiency, damages to cells during the fabrication, size
to make biocompatible materials (together with some control, and mechanical property of the fabricated fibers
other materials) pass through narrow channels or pipes, should be well considered.
and finally fabricate the fibers close to the outlet by
solidification. The microfluidic manufacturing method is 3.3. Cell-laden 2D modules
recognized as an efficient solution, as shown in Figure 2B Compared with the 1D cell spheroids and fibers
derived from the paper by Onoe et al. , which depicts an embedded cells, 2D modules with designed geometry
[30]
advanced fiber manufacturing process. The extracellular could accelerate the following assembling process. For
matrix protein with cells in the pre-gel state is covered by example, assembling the ring-shaped 2D modules to
stiff Ca-alginate hydrogel formed by the chemical reaction microvascular structures could be more efficient than
between the Na-alginate solution and the CaCl solution. assembling the spheroids. Nowadays, photolithography
2
Since the alginate in the outer layer forms a shell to avoid and soft lithography are commonly utilized in the
the diffusion of the inner extracellular matrix protein gel, fabrication of 2D modules with arbitrary shapes.
the cells inside can proliferate and form the cell-embedded Figure 2C shows the fabrication of cell-laden microplates
fibers under suitable conditions. Finally, the outer using photolithography [38,39] . The expected microplate is
alginate shell is removed with enzymes, and the fibers composed of the cell-adhesion layer, the core layer, and
as the building blocks in “bottom-up” tissue engineering the sacrificial layer. During the manufacturing process,
can be obtained. In addition to the method of microfluidic first, the core layer with a metal plate is covered to ensure
6 International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 3