Page 33 - IJB-7-4
P. 33
Lu, et al.
to fabricate. With the development of technology, the thus, the nature of plastic is often determined by the resin
modern bolus based on polymers has begun to appear in due to its large content. According to the physicochemical
the field of radiotherapy. Compared to other materials, properties of various plastics, they can be divided into
soft polymers are more suitable for constructing the two types: thermosetting plastics and thermoplastics.
modern bolus due to their unique physical properties, Thermoplastics melt when heated, cure when cooled, and
such as toughness, flexibility, and viscoelasticity. Young’s melt again when heated. Up to now, several thermoplastics
modulus is a key parameter used for defining soft and including polystyrene, acrylonitrile butadiene styrene
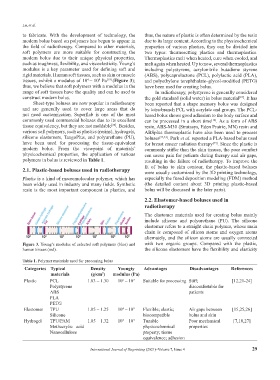
rigid materials. Human soft tissues, such as skin or muscle (ABS), polycaprolactone (PCL), polylactic acid (PLA),
tissues, exhibit a modulus of 10 – 10 Pa [19] (Figure 3); and polyethylene terephthalate–glycol-modified (PETG)
4
9
thus, we believe that soft polymers with a modulus in the have been used for creating bolus.
range of soft tissues have the quality and can be used to In radiotherapy, polystyrene is generally considered
construct modern bolus. the gold standard (solid water) in bolus material . It has
[21]
Sheet-type boluses are now popular in radiotherapy been reported that a shape memory bolus was designed
and are generally used to cover large areas that do by tetra-branch PCL with acrylate end groups. The PCL-
not need customization. Superflab is one of the most based bolus shows good adhesion to the body surface and
commonly used commercial boluses due to its excellent can be processed in a short time . As a form of ABS
[12]
tissue equivalency, but they are not moldable . Besides, resin, ABS-M30 (Stratasys, Eden Prairie, MN) resin and
[20]
various soft polymers, such as plastics (resins), hydrogels, ABSplus thermoplastic have also been used to process
silicone elastomers, TangoPlus, and polyurethane (PU), boluses [22,23] . Park et al. reported a PLA-based bolus used
have been used for processing the tissue-equivalent for breast cancer radiation therapy . Since the plastic is
[24]
modern bolus. From the viewpoint of materials’ commonly stiffer than the skin tissues, the poor comfort
physicochemical properties, the application of various can cause pain for patients during therapy and air gaps,
polymers in bolus is reviewed in Table 1. resulting in the failure of radiotherapy. To improve the
fit of bolus to skin contour, the plastic-based boluses
2.1. Plastic-based boluses used in radiotherapy were usually customized by the 3D printing technology,
Plastic is a kind of macromolecular polymer, which has especially the fused deposition modeling (FDM) method
been widely used in industry and many fields. Synthetic (the detailed content about 3D printing plastic-based
resin is the most important component in plastics, and bolus will be discussed in the later parts).
2.2. Elastomer-based boluses used in
radiotherapy
The elastomer materials used for creating bolus mainly
include silicone and polyurethane (PU). The silicone
elastomer refers to a straight chain polymer, whose main
chain is composed of silicon atoms and oxygen atoms
alternately, and the silicon atoms are usually connected
Figure 3. Young’s modulus of selected soft polymers (blue) and with two organic groups. Compared with the plastic,
human tissues (red). the silicone elastomers have the flexibility and elasticity
Table 1. Polymer materials used for processing bolus
Categories Typical Density Youngty Advantages Disadvantages References
materials (g/cm ) modulus (Pa)
3
Plastic PCL 1.03 – 1.30 10 – 10 7 Suitable for processing Stiff; [12,21-24]
6
Polystyrene discomfortable for
ABS patients
PLA
PETG
Elastomer TPU 1.05 – 1.25 10 – 10 9 Flexible; elastic; Air gaps between [15,25,26]
4
Silicone biocompatible bolus and skin
Hydrogel TPU/PAM 1.05 – 1.32 10 – 10 4 Tunable Poor mechanical [7,10,27]
2
Methacrylic acid physicochemical properties
Nanocellulose property; tissue
equivalence; adhesion
International Journal of Bioprinting (2021)–Volume 7, Issue 4 29