Page 201 - IJB-8-3
P. 201
Rodriguez-Salvador, et al.
published between January 1, 2015, and December 31,
2021. The collected publications were first manually
classified based on specific applications of tissue
spheroids in general. Next, publications describing the
use of tissue spheroids as building blocks were selected
manually for further analysis.
Collected publications underwent scientometric
analysis. First, subject areas were determined based
on Scopus subject categorization. The growth kinetics
of publication activity within the retrieval period was Figure 1. Distribution of scientific publications based on the
identified, as were the most prolific countries, cities, method employed to build tissue spheroids used as building blocks.
journals, and institutions. The most cited articles were
determined as well.
3. Results
In total, 777 publications from Scopus were retrieved for
the period between January 1, 2015, and December 31,
2021, on tissue spheroids in general. After identifying the
publications that focused on tissue spheroids as building
blocks, a total of 177 publications were obtained. These
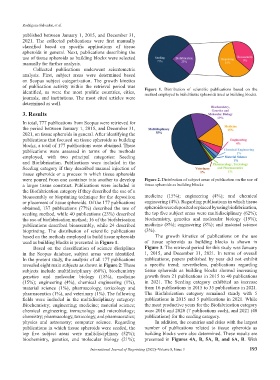
publications were assessed in terms of the methods
employed, with two principal categories: Seeding
and Biofabrication. Publications were included in the
Seeding category if they described manual injection of
tissue spheroids or a process in which tissue spheroids
were poured from one container into another to develop Figure 2. Distribution of subject areas of publication on the use of
a larger tissue construct. Publications were included in tissue spheroids as building blocks.
the Biofabrication category if they described the use of a
bioassembly or bioprinting technique for the deposition medicine (15%); engineering (4%); and chemical
or placement of tissue spheroids. Of the 177 publications engineering (4%). Regarding publications in which tissue
obtained, 137 publications (77%) described the use of spheroids were deposited or placed by using biofabrication,
seeding method, while 40 publications (23%) described the top five subject areas were multidisciplinary (62%);
the use of biofabrication method; 16 of the biofabrication biochemistry, genetics and molecular biology (19%);
publications described bioassembly, while 24 described medicine (8%); engineering (8%); and material science
bioprinting. The distribution of scientific publications (3%).
based on the methods employed to build tissue spheroids The growth kinetics of publications on the use
used as building blocks is presented in Figure 1. of tissue spheroids as building blocks is shown in
Based on the classification of science disciplines Figure 3. The retrieval period for this study was January
in the Scopus database, subject areas were identified. 1, 2015, and December 31, 2021. In terms of overall
In the present study, the analysis of all 177 publications publications, papers published by year did not exhibit
revealed eight main subjects as shown in Figure 2: These a specific trend; nevertheless, publications regarding
subjects include multidisciplinary (60%), biochemistry tissue spheroids as building blocks showed increasing
genetics and molecular biology (18%), medicine growth from 21 publications in 2015 to 40 publications
(15%); engineering (4%), chemical engineering (1%), in 2021. The Seeding category exhibited an increase
material science (1%), pharmacology, toxicology and from 16 publications in 2015 to 35 publications in 2021.
pharmaceutics (1%), and veterinary (1%). The following The Biofabrication category remained steady with 5
fields were included in the multidisciplinary category: publications in 2015 and 5 publications in 2021. While
Biochemistry; engineering; medicine; material science; the most productive years for the Biofabrication category
chemical engineering; immunology and microbiology; were 2016 and 2020 (7 publications each), and 2021 (40
chemistry; pharmacology, toxicology, and pharmaceutics; publications) for the seeding category.
physics and astronomy; computer science. Regarding In addition, the countries and cities with the largest
publications in which tissue spheroids were seeded, the number of publications related to tissue spheroids as
top five subject areas were multidisciplinary (52%); building blocks were also determined. These results are
biochemistry, genetics, and molecular biology (21%); presented in Figures 4A, B, 5A, B, and 6A, B. With
International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 3 193