Page 333 - IJB-8-4
P. 333
Mancilla-De-la-Cruz, et al.
(2) Filament extrusion the print nozzle, following which they are dried .
[10]
Filament extrusion is the technique of using rollers to feed Pressure-assisted microsyringes (PAM) are capable of
a solid polymer filament through a chamber with heating producing DDDs with a combination of materials of
[16]
elements which melt the polymer filament into a semi- drugs using multi-head extruders (Table 4) .
molten state, following which it is ejected from the end of 2.3. Vat photopolymerization
a nozzle or orifice. Following ejection, the polymer cools
and solidifies on the substrate, allowing further layers to Vat photopolymerization can be defined as the process in
be deposited on top (Table 3) [10,16] . which liquid photopolymer in a vat is selectively cured
by light-activated polymerization (Figure 4). It comes
[9]
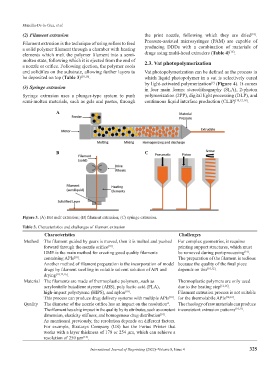
(3) Syringe extrusion in four main forms: stereolithography (SLA), 2-photon
Syringe extrusion uses a plunger-type system to push polymerization (2PP), digital light processing (DLP), and
semi-molten materials, such as gels and pastes, through continuous liquid interface production (CLIP) [10,12,16] .
A
B C
Figure 3. (A) Hot melt extrusion; (B) filament extrusion; (C) syringe extrusion.
Table 3. Characteristics and challenges of filament extrusion
Characteristics Challenges
Method The filament guided by gears is moved, then it is melted and pushed For complex geometries, it requires
forward through the nozzle orifice . printing support structures, which must
[10]
HME is the main method for creating good quality filaments be removed during post-processing .
[16]
containing APIs . The preparation of the filament is tedious
[10]
Another method of filament preparation is the incorporation of model because the quality of the final piece
drugs by filament swelling in volatile solvent solution of API and depends on this [10,12] .
drying [10,12,16] .
Material The filaments are made of thermoplastic polymers, such as Thermoplastic polymers are only used
acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), poly lactic acid (PLA), due to the heating step [12,16] .
high-impact polystyrene (HIPS), and nylon . Filament extrusion process is not suitable
[10]
This process can produce drug delivery systems with multiple APIs . for the thermolabile APIs [12,16] .
[16]
Quality The diameter of the nozzle orifice has an impact on the resolution . The rheology of raw materials can produce
A
The filament has a big impact in the quality by its attributes, such as constant inconsistent extrusion patterns [10,11] .
dimension, elasticity stiffness, and homogenous drug distribution .
[10]
As mentioned previously, the resolution depends on different factors.
For example, Stratasys Company (US) has the Fortus Printer that
works with a layer thickness of 178 or 254 μm, which can achieve a
resolution of 250 μm .
[18]
International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 4 325