Page 233 - IJB-9-2
P. 233
International Journal of Bioprinting Coronary and peripheral artery disease. State of the art.
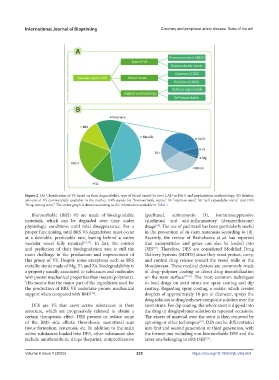
Figure 2. (A) Classification of VS based on their degradability, type of blood vessel (to treat CAD or PAD) and implantation methodology. (B) Relative
amount of VS commercially available in the market. BRS stands for “bioresorbable stents,” SS “stainless steel,” SE “self-expandable stent,” and DES
“drug-eluting stent.” The sector graph is drawn according to the information available in Table 1.
Bioresorbable (BRS) VS are made of biodegradable (paclitaxel, actinomycin D), immunosuppressive
materials, which can be degraded over time under (sirolimus) and anti-inflammatory (dexamethasone)
physiologic conditions until total disappearance. For a drugs . The use of paclitaxel has been particularly useful
[18]
proper functioning, total BRS VS degradation must occur in the prevention of in-stent restenosis according to [8].
at a desirable, predictable rate, leaving behind a native Recently, the review of Beshchasna et al. has reported
vascular vessel fully repaired [15,17] . In fact, the control that nanoparticles and genes can also be loaded into
and prediction of their biodegradation rate is still the DES . Therefore, DES are considered Modified Drug
[15]
main challenge in the production and improvement of Delivery Systems (MDDS) since they must protect, carry,
this group of VS. Despite some exceptions such as BRS and control drug release toward the vessel walls or the
metallic stents made of Mg, Ti, and Zn, biodegradability is bloodstream. These medical devices are commonly made
a property usually associated to substances and molecules of drug–polymer coating or direct drug immobilization
with poorer mechanical properties than metals (polymers). on the stent surface [15,18] . The most common techniques
This means that the major part of the ingredients used for to load drugs on stent struts are spray coating and dip
the production of BRS VS undertake poorer mechanical coating. Regarding spray coating, a nozzle, which creates
support when compared with BMS . droplets of approximately 10 μm in diameter, sprays the
[12]
drug solution or drug/polymer composite solution over the
DES are VS that carry active substances in their stent struts. For dip coating, the whole stent is dipped into
structure, which are progressively released to obtain a the drug or drug/polymer solution in repeated occasions.
certain therapeutic effect. DES prevent or reduce some The excess of material over the stent is then removed by
of the BMS side effects: thrombosis, neointimal scar spinning or other techniques . DES can be differentiated
[19]
tissue formation, restenosis, etc. In addition to the main into first and second generation or third generation, with
active substances loaded into DES, other substances also the former one including non-bioresorbable DES and the
include antithrombotic drugs (heparin), antiproliferative latter one belonging to BRS DES .
[15]
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 225 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.664