Page 238 - IJB-9-2
P. 238
International Journal of Bioprinting Coronary and peripheral artery disease. State of the art.
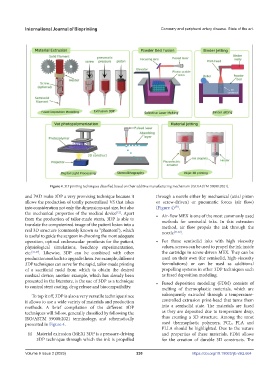
Figure 4. 3D printing techniques classified based on their additive manufacturing mechanism (ISO/ASTM 59000:2021).
and PAD make 3DP a very promising technique because it through a nozzle either by mechanical (axial piston
allows the production of totally personalized VS that takes or screw-driven) or pneumatic forces (air flow)
[51]
into consideration not only the dimensions and size, but also (Figure 4) .
[12]
the mechanical properties of the medical device . Apart • Air-flow MEX is one of the most commonly used
from the production of tailor-made stents, 3DP is able to methods for semisolid inks. In this extrusion
translate the computerized image of the patient lesion into a method, air flow propels the ink through the
real 3D structure (commonly known as “phantom”), which nozzle [51,52] .
is useful to guide the surgeon in choosing the most adequate
operation, optimal endovascular prosthesis for the patient, • For those semisolid inks with high viscosity
physiological simulations, benchtop experimentation, values, screws can be used to propel the ink inside
etc. [41-47] . Likewise, 3DP can be combined with other the cartridge in screw-driven MEX. They can be
production methods to upgrade them. For example, different used on their own (for semisolid, high-viscosity
3DP techniques can serve for the rapid, tailor-made printing formulations) or can be used as additional
of a sacrificial mold from which to obtain the desired propelling systems in other 3DP techniques such
medical device; another example, which has already been as fused deposition modeling.
presented in the literature, is the use of 3DP as a technique • Fused deposition modeling (FDM) consists of
to control stent coating, drug release and biocompatibility. melting of thermoplastic materials, which are
To top it off, 3DP is also a very versatile technique since subsequently extruded through a temperature-
it allows to use a wide variety of materials and production controlled extrusion print-head that turns them
methods. A brief compilation of the different 3DP into a semisolid state. The materials are fused
techniques will follow, generally classified by following the as they are deposited due to temperature drop,
ISO/ASTM 59000:2021 terminology, and schematically thus creating a 3D structure. Among the most
presented in Figure 4. used thermoplastic polymers, PCL, PLA and
PLLA should be highlighted. Due to the nature
(i) Material extrusion (MEX) 3DP is a pressure-driving and properties of these materials, FDM allows
3DP technique through which the ink is propelled for the creation of durable 3D constructs. The
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 230 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.664