Page 242 - IJB-9-2
P. 242
International Journal of Bioprinting Coronary and peripheral artery disease. State of the art.
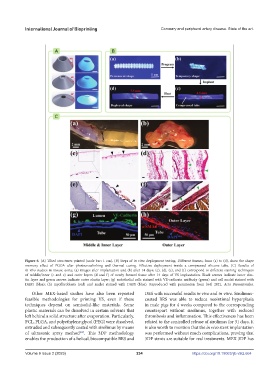
Figure 6. (A) Tilted structures printed (scale bar: 1 cm). (B) Steps of in vitro deployment testing. Different frames, from (a) to (d), show the shape
memory effect of PGDA after photocrosslinking and thermal curing. Effective deployment inside a compressed silicone tube. (C) Results of
in vivo studies in mouse aorta; (a) images after implantation and (b) after 14 days; (c), (d), (e), and (f) correspond to different staining techniques
of middle/inner (c and e) and outer layers (d and f) of newly formed tissue after 14 days of VS implantation. Black arrows indicate inner elas-
tin layer and green arrows indicate outer elastin layer; (g) endothelial cells stained with VE-cadherin antibody (green) and cell nuclei stained with
DAPI (blue); (h) myofibroblasts (red) and nuclei stained with DAPI (blue). Reproduced with permission from [64] 2021, Acta Biomaterialia.
Other MEX-based studies have also been reported DES with successful results in vivo and in vitro. Sirolimus-
feasible methodologies for printing VS, even if these coated BRS was able to reduce neointimal hyperplasia
techniques depend on semisolid-like materials. Some in male pigs for 4 weeks compared to the corresponding
plastic materials can be dissolved in certain solvents that counterpart without sirolimus, together with reduced
left behind a solid structure after evaporation. Particularly, thrombosis and inflammation. This effectiveness has been
PCL, PLGA, and polyethylene glycol (PEG) were dissolved, related to the controlled release of sirolimus for 31 days. It
extruded and subsequently coated with sirolimus by means is also worth to mention that the in vivo stent implantation
of ultrasonic spray method . This 3DP methodology was performed without much complications, proving that
[69]
enables the production of a helical, biocompatible BRS and 3DP stents are suitable for real treatments. MEX 3DP has
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 234 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.664