Page 245 - IJB-9-2
P. 245
International Journal of Bioprinting Coronary and peripheral artery disease. State of the art.
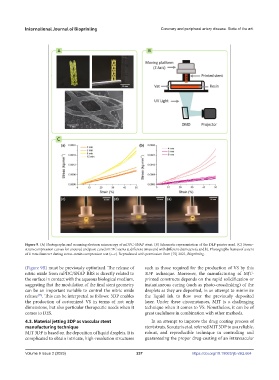
Figure 9. (A) Photographs and scanning electron microscopy of mDPC-SNAP stent. (B) Schematic representation of the DLP printer used. (C) Stress–
strain compression curves for uncured and post-cured mPDC stents at different times and with different diameters (a and b). Photographs frames of a stent
of 6 mm diameter during stress–strain compression test (c–e). Reproduced with permission from [75] 2021, Bioprinting.
(Figure 9B) must be previously optimized. The release of such as those required for the production of VS by this
nitric oxide from mPDC/SNAP BRS is directly related to 3DP technique. Moreover, the manufacturing of MJT-
the surface in contact with the aqueous biological medium, printed constructs depends on the rapid solidification or
suggesting that the modulation of the final stent geometry instantaneous curing (such as photo-crosslinking) of the
can be an important variable to control the nitric oxide droplets as they are deposited, in an attempt to minimize
[75]
release . This can be interpreted as follows: 3DP enables the liquid ink to flow over the previously deposited
the production of customized VS in terms of not only layer. Under these circumstances, MJT is a challenging
dimensions, but also particular therapeutic needs when it technique when it comes to VS. Nonetheless, it can be of
comes to DES. great usefulness in combination with other methods.
4.3. Material jetting 3DP as vascular stent In an attempt to improve the drug coating process of
manufacturing technique stent struts, Scoutaris et al. referred MJT 3DP to as a reliable,
MJT 3DP is based on the deposition of liquid droplets. It is robust, and reproducible technique in controlling and
complicated to obtain intricate, high-resolution structures guaranteeing the proper drug-coating of an intravascular
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 237 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.664