Page 249 - IJB-9-2
P. 249
International Journal of Bioprinting Coronary and peripheral artery disease. State of the art.
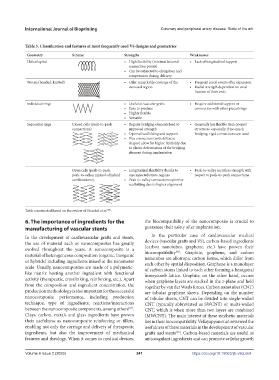
Table 3. Classification and features of most frequently used VS designs and geometries
Geometry Scheme Strengths Weaknesses
Helical spiral • High flexibility (minimal internal • Lack of longitudinal support
connection points)
• Can be subjected to elongation and
compression during delivery
Woven (braided, knitted) • Offer remarkable coverage of the • Frequent recoil events after expansion
stenosed region • Radial strength dependent on axial
fixation of their ends
Individual rings • Useful as vascular grafts • Require additional support or
• Easy to produce connection with other pieces/rings
• Highly flexible
• Versatile
Sequential rings Closed cells (peak-to-peak • Regular bridging elements lead to • Generally less flexible than opened
connections) improved strength structures, especially if too much
• Optimal scaffolding and support bridging, rigid connections are used
• Flex connectors (with different
shapes) allow for higher flexibility due
to plastic deformation of the bridging
element during implantation
Open cells (peak-to-peak, • Longitudinal flexibility thanks to • Peak-to-valley sacrifices strength with
peak-to-valley, myriad of hybrid unconnected struts regions respect to peak-to-peak connections
combinations). • Peak-to-valley connections optimize
scaffolding due to higher alignment
Table constructed based on the review of Stoeckel et al. .
[28]
6. The importance of ingredients for the the biocompatibility of the nanocomposite is crucial to
manufacturing of vascular stents guarantee their safety after implantation.
In the development of cardiovascular grafts and stents, In the particular case of cardiovascular medical
the use of material such as nanocomposites has greatly devices (vascular grafts and VS), carbon-based ingredients
evolved throughout the years. A nanocomposite is a (carbon nanotubes, graphene, etc.) have proven their
[86]
material of heterogeneous composition (organic, inorganic biocompatibility . Graphite, graphene, and carbon
nanotubes are allotropic carbon forms, which differ from
or hybrids) including ingredients mixed at the nanometer each other by spatial disposition. Graphene is a monolayer
scale. Usually, nanocomposites are made of a polymeric- of carbon atoms linked to each other forming a hexagonal
like matrix hosting another ingredient with functional honeycomb lattice. Graphite, on the other hand, occurs
activity (therapeutic, crosslinking, reinforcing, etc.). Apart when graphene layers are stacked in the z-plane and held
from the composition and ingredient concentration, the together by van der Waals forces. Carbon nanotubes (CNT)
production methodology is also important for the successful are tubular graphene sheets. Depending on the number
nanocomposite performance, including production of tubular sheets, CNT can be divided into single-walled
technique, type of ingredients, reactions/interactions CNT (typically abbreviated as SWCNT) or multi-walled
between the nanocomposite components, among others . CNT, which is when more than two layers are combined
[86]
Clays, carbon, metals and glass ingredients have proven (MWCNT). The main interest of these synthetic materials
their usefulness as nanocomposite reinforcing or fillers, lies in their biocompatibility. Vellayappan et al. reviewed the
enabling not only the carriage and delivery of therapeutic usefulness of these materials in the development of vascular
ingredients, but also the improvement of mechanical grafts and stents . Carbon-based materials are useful as
[86]
features and rheology. When it comes to medical devices, anticoagulant ingredients and can promote cellular growth
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 241 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.664