Page 160 - IJB-9-4
P. 160
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D printing and 3D-printed electronics in smart drug delivery devices
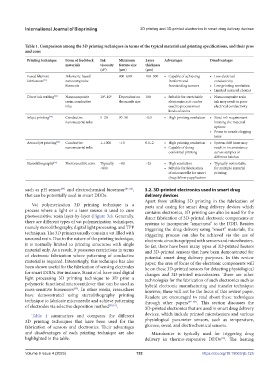
Table 1. Comparison among the 3D printing techniques in terms of the typical material and printing specifications, and their pros
and cons
Printing technique Form of feedstock Ink Minimum Layer Advantages Disadvantages
materials viscosity feature size thickness
(cP) (µm) (µm)
Fused filament Polymeric-based – 400–600 100–300 • Capable of achieving • Low electrical
fabrication [92] nanocomposite freeform and conductivity
filaments freestanding sensors • Low printing resolution
• Limited material choices
Direct ink writing [93] Nanocomposite 10 –10 6 Dependent on 100 • Suitable for stretchable • Nanocomposite resin
2
resin, conductive the nozzle size electronics as it can be ink may result in poor
inks used to process most electrical conductivity
kinds of resins
Inkjet printing [94] Conductive 5–20 30–50 <0.5 • High printing resolution • Strict ink requirement
nanomaterial inks limiting the material
options
• Prone to nozzle clogging
issue
Aerosol jet printing [94] Conductive 1–1000 ~10 0.1–2 • High printing resolution • System drift issue may
nanomaterial inks • Capable of doing result in inconsistency
conformal printing across samples of
different batches
Stereolithography [95] Photosensitive resin Typically ~80 ~25 • High resolution • Typically not suitable
<600 • Suitable for fabrication for multiple material
of microneedle for smart printing
drug delivery application
such as pH sensor and electrochemical biosensor [85-88] , 3.2. 3D-printed electronics used in smart drug
[84]
that can be potentially used in smart DDDs. delivery devices
Apart from utilizing 3D printing in the fabrication of
Vat polymerization 3D printing technique is a parts and casing for smart drug delivery devices which
process where a light or a laser source is used to cure contains electronics, 3D printing can also be used for the
photosensitive resin layer-by-layer (Figure 3e). Generally, direct fabrication of 3D-printed electronic components or
there are different types of vat polymerization techniques, systems to incorporate “smartness” to the DDD. Besides
namely stereolithography, digital light processing, and TPP triggering the drug delivery using “smart” materials, the
techniques. The 3D printers usually contain a vat filled with triggering process can also be achieved via the use of
uncured resin. Due to the nature of the printing technique, electronic circuits equipped with sensors and microheaters.
it is normally limited to printing structures with single So far, there have been many types of 3D-printed heaters
material only. As a result, it possesses restrictions in terms and 3D-printed sensors that have been demonstrated for
of electronic fabrication where patterning of conductive potential smart drug delivery purposes. In this review
material is required. Interestingly, this technique has also paper, the area of focus of the electronic components will
been shown useful for the fabrication of sensing electrodes be on these 3D-printed sensors for detecting physiological
for smart DDDs. For instance, Stassi et al. have used digital changes and 3D-printed microheaters. There are other
light processing 3D printing technique to 3D print a technologies for the fabrication of such electronics such as
polymeric functional microcantilever that can be used as hybrid electronic manufacturing and transfer technique;
mass-sensitive biosensors . In other works, researchers however, these will not be the focus of this review paper.
[89]
have demonstrated using stereolithography printing Readers are encouraged to read about these techniques
technique to fabricate microneedle and achieve patterning through other papers [99-104] . This section discusses the
of electrodes via selective deposition method [90,91] . 3D-printed electronics that are used in smart drug delivery
Table 1 summarizes and compares the different devices, which include printed microheaters and various
3D printing techniques that have been used for the physiological parameter sensors, such as temperature,
fabrication of sensors and electronics. Their advantages glucose, sweat, and electrochemical sensors.
and disadvantages of each printing technique are also Microheater is typically used for triggering drug
highlighted in the table. delivery in thermo-responsive DDDs . The heating
[10]
Volume 9 Issue 4 (2023) 152 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.725