Page 12 - IJB-9-6
P. 12
International Journal of Bioprinting Electrospinning PETG
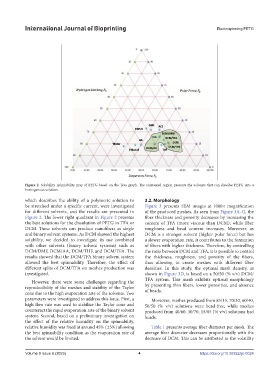
Figure 2. Solubility–spinnability map of PETG based on the Teas graph. The contoured region presents the solvents that can dissolve PETG into a
homogenous solution.
which describes the ability of a polymeric solution to 3.2. Morphology
be stretched under a specific current, were investigated Figure 3 presents SEM images at 1000× magnification
for different solvents, and the results are presented in of the produced meshes. As seen from Figure 3A–G, the
Figure 2. The lower right quadrant in Figure 2 presents fiber thickness and porosity decreases by increasing the
the best solutions for the dissolution of PETG in TFA or content of TFA (more viscous than DCM), while fiber
DCM. These solvents can produce nanofibers as single roughness and bead content increases. Moreover, as
and binary solvent systems. As DCM showed the highest DCM is a stronger solvent (higher polar force) but has
solubility, we decided to investigate its use combined a slower evaporation rate, it contributes to the formation
with other solvents (binary solvent systems) such as of fibers with higher thickness. Therefore, by controlling
DCM/DMF, DCM/AA, DCM/THF, and DCM/TFA. The the ratio between DCM and TFA, it is possible to control
results showed that the DCM/TFA binary solvent system the thickness, roughness, and porosity of the fibers,
allowed the best spinnability. Therefore, the effect of thus allowing to create meshes with different fiber
different splits of DCM/TFA on meshes production was densities. In this study, the optimal mesh density, as
investigated. shown in Figure 3D, is based on a 50/50 (% v/v) DCM/
TFA system. This mesh exhibits optimal morphology
However, there were some challenges regarding the
reproducibility of the meshes and stability of the Taylor by presenting thin fibers, lower porosities, and absence
cone due to the high evaporation rate of the solvents. Two of beads.
parameters were investigated to address this issue. First, a Moreover, meshes produced from 85/15, 70/30, 60/40,
high flow rate was used to stabilize the Taylor cone and 50/50 (% v/v) solutions were bead-free, while meshes
counteract the rapid evaporation rate of the binary solvent produced from 40/60, 30/70, 15/85 (% v/v) solutions had
system. Second, based on a preliminary investigation on beads.
the effect of the relative humidity on the spinnability,
relative humidity was fixed at around 45% (±5%) allowing Table 1 presents average fiber diameter per mesh. The
the best spinnability condition as the evaporation rate of average fiber diameter decreases proportionally with the
the solvent would be limited. decrease of DCM. This can be attributed to the volatility
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0024