Page 110 - IJPS-10-4
P. 110
International Journal of
Population Studies Climate change-induced human mobility
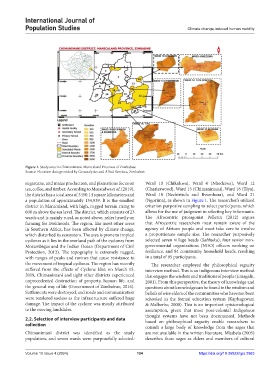
Figure 1. Study area in Chimanimani, Manicaland Province of Zimbabwe
Source: Elevation data provided by Geoanalytics and Allied Services, Zimbabwe.
sugarcane, and maize production, and plantations focus on Ward 10 (Chikukwa), Ward 4 (Nhedziwa), Ward 12
tea, coffee, and timber. According to Mutandwa et al. (2019), (Charleswood), Ward 15 (Chimanimani), Ward 16 (Tiya),
the district has a total area of 3450.14 square kilometers and Ward 18 (Nechirinda and Bvumbura), and Ward 21
a population of approximately 134,939. It is the smallest (Ngorima), as shown in Figure 1. The researcher’s utilized
district in Manicaland, with high, rugged terrain rising to criterion purposive sampling to select participants, which
600 m above the sea level. The district, which consists of 23 allows for the use of judgment in selecting key informants.
wards and is mainly rural, as noted above, relies heavily on The Afrocentric protagonist Pellerin (2012) argues
farming for livelihoods. The region, like most other areas that Afrocentric researchers must remain aware of the
in Southern Africa, has been affected by climate change, agency of African people and must take care to involve
which disturbed its ecosystem. The area is prone to tropical a proportionate sample size. The researcher purposively
cyclones as it lies in the overland path of the cyclones from selected seven village heads (Sabhuku), four senior non-
Mozambique and the Indian Ocean (Department of Civil governmental organizations (NGO) officers working on
Protection, 2013). The topography is extremely rugged, resilience, and 84 community household heads, resulting
with ranges of peaks and ravines that cause resistance to in a total of 95 participants.
the movement of tropical cyclones. The region has recently The researcher employed the philosophical sagacity
suffered from the effects of Cyclone Idai; on March 15, interview method. This is an indigenous interview method
2019, Chimanimani and eight other districts experienced that engages the wisdom and traditions of people (Emagalit,
unprecedented destruction of property, human life, and 2001). From this perspective, the theory of knowledge and
the general way of life (Government of Zimbabwe, 2016). questions about knowledge can be found in the wisdom and
Settlements were destroyed, and roads and communication beliefs of wise elders of the communities who have not been
were rendered useless as the infrastructure suffered huge schooled in the formal education system (Kaphagawani
damage. The impact of the cyclone was mostly attributed & Malherbe, 2000). This is an important epistemological
to the moving landslides. assumption, given that most post-colonial Indigenous
thought systems have not been documented. Methods
2.2. Selection of interview participants and data based on philosophical sagacity enable researchers to
collection
consult a large body of knowledge from the sages that
Chimanimani district was identified as the study are not available in the written literature. Mkabela (2005)
population, and seven wards were purposefully selected: describes these sages as elders and members of cultural
Volume 10 Issue 4 (2024) 104 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.2983