Page 145 - IJPS-11-5
P. 145
International Journal of
Population Studies Fertility desire of married women
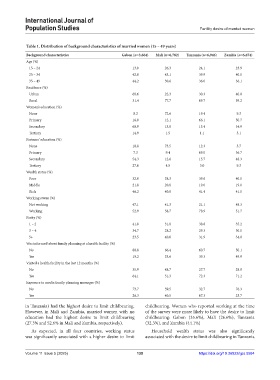
Table 1. Distribution of background characteristics of married women (15 – 49 years)
Background characteristics Gabon (n=3,664) Mali (n=6,782) Tanzania (n=6,946) Zambia (n=6,674)
Age (%)
15 – 24 13.0 26.3 24.1 23.9
25 – 34 42.8 43.1 39.9 40.0
35 – 49 44.2 30.6 36.0 36.1
Residence (%)
Urban 68.6 22.3 30.3 40.8
Rural 31.4 77.7 69.7 59.2
Women’s education (%)
None 8.2 72.6 19.4 9.3
Primary 16.0 12.1 66.1 50.7
Secondary 60.9 13.8 13.4 34.9
Tertiary 14.9 1.5 1.1 5.1
Partners’ education (%)
None 10.8 73.5 12.3 5.7
Primary 7.3 9.4 69.0 36.7
Secondary 54.3 12.6 15.7 48.3
Tertiary 27.6 4.5 3.0 9.3
Wealth status (%)
Poor 32.0 38.3 39.6 40.0
Middle 21.8 20.8 19.0 19.0
Rich 46.2 40.8 41.4 41.0
Working status (%)
Not working 47.1 41.3 21.1 48.3
Working 52.9 58.7 78.9 51.7
Parity (%)
1 – 2 41.8 31.8 38.8 35.2
3 – 4 34.7 28.2 29.3 30.0
5+ 23.5 40.0 31.9 34.8
Was informed about family planning at a health facility (%)
No 80.8 66.4 60.7 50.1
Yes 19.2 33.6 39.3 49.9
Visited a health facility in the last 12 months (%)
No 35.9 48.7 27.7 28.8
Yes 64.1 51.3 72.3 71.2
Exposure to media family planning messages (%)
No 73.7 59.5 32.7 76.3
Yes 26.3 40.5 67.3 23.7
in Tanzania) had the highest desire to limit childbearing. childbearing. Women who reported working at the time
However, in Mali and Zambia, married women with no of the survey were more likely to have the desire to limit
education had the highest desire to limit childbearing childbearing: Gabon (35.6%), Mali (26.6%), Tanzania
(27.3% and 52.6% in Mali and Zambia, respectively). (32.3%), and Zambia (44.1%)
As expected, in all four countries, working status Household wealth status was also significantly
was significantly associated with a higher desire to limit associated with the desire to limit childbearing in Tanzania
Volume 11 Issue 5 (2025) 139 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.5584