Page 32 - IJPS-7-2
P. 32
International Journal of
Population Studies Gender gap in life expectancy in South and East Europe
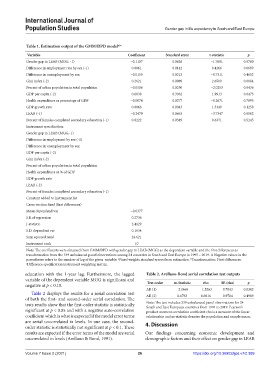
Table 1. Estimation output of the GMM/DPD model abc
Variable Coefficient Standard error t‑statistic p
Gender gap in LEAB (MGG, -1) −0.1107 0.0626 −1.7681 0.0780
Difference in employment rate by sex (-1) 0.0061 0.0142 0.4266 0.6699
Difference in unemployment by sex −0.0155 0.0212 −0.7311 0.4652
Gini index (-2) 0.2621 0.0989 2.6509 0.0084
Percent of urban population in total population −0.0506 0.0250 −2.0253 0.0436
GDP per capita (-2) 0.6038 0.3032 1.9913 0.0473
Health expenditure as percentage of GDP −0.0074 0.0277 −0.2671 0.7895
GDP growth rate 0.0066 0.0043 1.5349 0.1258
LEAB (-1) −0.2479 0.0663 −3.7347 0.0002
Percent of females completed secondary education (-1) 0.0222 0.0349 0.6371 0.5245
Instrument specification:
Gender gap in LEAB (MGG,-1)
Difference in employment by sex (-1)
Difference in unemployment by sex
GDP per capita (-2)
Gini index (-2)
Percent of urban population in total population
Health expenditure as % of GDP
GDP growth rate
LEAB (-2)
Percent of females completed secondary education (-1)
Constant added to Instrument list
Cross-section fixed (first differences)
Mean dependend var −0.0377
S.E.of regression 0.2736
J-statistic 2.4129
S.D. dependent var 0.1634
Sum squared resid 24.621
Instrument rank 10
Note: The coefficients were obtained from GMM/DPD with gender gap in LEAB (MGG) as the dependent variable and the first differences as
transformation from the 339 unbalanced panel observations among 24 countries in South and East Europe in 1995 – 2019. A Negative values in the
parentheses refers to the number of lag of the given variable. Fixed weights standard errors from estimation. Transformation: First differences.
b
a
c Difference specification instrument weighting matrix.
education with the 1-year lag. Furthermore, the lagged Table 2. Arellano‑Bond serial correlation test outputs
variable of the dependent variable MGG is significant and Test order m‑Statistic rho SE (rho) p
negative at p < 0.10.
AR (1) −2.1669 −1.5263 0.7043 0.0302
Table 2 displays the results for a serial correlation test AR (2) 0.6763 0.6616 0.9784 0.4989
of both the first- and second-order serial correlation. The
tests results show that the first-order statistic is statistically Note: The test includes 339 unbalanced panel observations for 24
South and East European countries from 1994 to 2019. Pearson’s
significant at p < 0.05 and with a negative auto-correlation product moment correlation coefficient rho is a measure of the linear
coefficient which is what is expected if the model error terms relationship and m-statistic denotes the population and sample mean.
are serial uncorrelated in levels. In our case, the second- 4. Discussion
order statistic is statistically not significant at p < 0.1. These
results are expected if the error terms of the model are serial Our findings concerning economic development and
uncorrelated in levels (Arellano & Bond, 1991). demographic factors and their effect on gender gap in LEAB
Volume 7 Issue 2 (2021) 26 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.v7i2.389