Page 23 - IJPS-9-2
P. 23
International Journal of
Population Studies Dominant drivers of inequalities in child survival
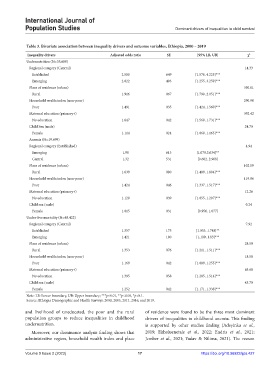
Table 3. Bivariate association between inequality drivers and outcome variables, Ethiopia, 2000 – 2019
Inequality drivers Adjusted odds ratio SE [95% LB, UB] χ 2
Undernutrition (N=35,688)
Regional category (Central) 14.33
Established 2.580 649 [1.576, 4.225]***
Emerging 2.022 493 [1.255, 3.259]***
Place of residence (urban) 350.61
Rural 1.916 067 [1.790, 2.051]***
Household wealth index (non-poor) 290.90
Poor 1.491 035 [1.424, 1.560]***
Maternal education (primary+) 392.42
No education 1.647 042 [1.568, 1.731]***
Child Sex (male) 24.70
Female 1.114 024 [1.068, 1.163]***
Anemia (N=19,699)
Regional category (Established) 4.94
Emerging 1.98 613 [1.079,3.634]**
Central 1.32 531 [0.602, 2.908]
Place of residence (urban) 102.09
Rural 1.639 080 [1.489, 1.804]***
Household wealth index (non-poor) 119.86
Poor 1.424 046 [1.337, 1.517]***
Maternal education (primary+) 12.26
No education 1.128 039 [1.055, 1.207]***
Child sex (male) 0.24
Female 1.015 031 [0.956, 1.077]
Under-five mortality (N=48,422)
Regional category (Central) 7.92
Established 1.357 175 [1.053, 1.748]**
Emerging 1.421 180 [1.109, 1.83]***
Place of residence (urban) 28.59
Rural 1.353 076 [1.211, 1.511]***
Household wealth index (non-poor) 18.58
Poor 1.169 042 [1.089, 1.255]***
Maternal education (primary+) 63.68
No education 1.395 058 [1.285, 1.514]***
Child sex (male) 43.70
Female 1.252 042 [1.171, 1.338]***
Note: LB: Lower boundary, UB: Upper boundary; ***p<0.01, **p<0.05, *p<0.1.
Source: Ethiopia Demographic and Health Surveys: 2000, 2005, 2011, 2016, and 2019.
and livelihood of uneducated, the poor and the rural of residence were found to be the three most dominant
population groups to reduce inequalities in childhood drivers of inequalities in childhood anemia. This finding
undernutrition. is supported by other studies finding (Adeyinka et al.,
Moreover, our dominance analysis finding shows that 2019; Ekholuenetale et al., 2022; Endris et al., 2021;
administrative region, household wealth index and place Jember et al., 2021; Yadav & Nilima, 2021). The reason
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 17 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.427