Page 35 - IJPS-9-2
P. 35
International Journal of
Population Studies COVID-19 and intersectionality in Brazil
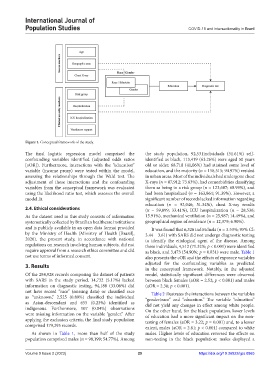
Figure 1. Conceptual framework of the study.
The final logistic regression model comprised the the study population, 92,531individuals (51.61%) self-
confounding variables identified (adjusted odds ratios identified as black, 113,419 (63.26%) were aged 50 years
[aOR]). Furthermore, interactions with the “education” old or older, 68,718 (41,06%) had attained some level of
variable (income proxy) were tested within the model, education, and the majority (n = 158,515; 94.97%) resided
assessing the relationships through the Wald test. The in urban areas. Most of the individuals had undergone chest
adjustment of these interactions and the confounding X-rays (n = 87,912; 73.63%), had comorbidities classifying
variables from the conceptual framework was evaluated them as being in a risk group (n = 123,687; 68.99%), and
using the likelihood ratio test, which assesses the overall had been hospitalized (n = 163,864; 91.39%). However, a
model fit. significant number of records lacked information regarding
education (n = 92,046; 51.34%), chest X-ray results
2.4. Ethical considerations (n = 59,899; 33.41%), ICU hospitalization (n = 28,536;
As the dataset used in this study consists of information 15.91%), mechanical ventilation (n = 25,987; 14.49%), and
systematically collected by Brazilian healthcare institutions geographical region of residence (n = 12,379; 6.90%).
and is publicly available in an open data format provided It was found that 6,326 individuals (n = 3.53%; 95% CI:
by the Ministry of Health (Ministry of Health [Brazil], 3.44 – 3.61) with SARS did not undergo diagnostic testing
2020), the present study, in accordance with national to identify the etiological agent of the disease. Among
regulations on research involving human subjects, did not these individuals, 4,512 (71.32%; p < 0.001) were identified
require approval from a research ethics committee and did as black, and 3,473 (54.90%; p = 0.831) were male. Table 1
not use terms of informed consent. also presents the cOR and the effects of exposure variables
3. Results adjusted for the confounding variables as predicted
in the conceptual framework. Notably, in the adjusted
Of the 284,928 records composing the dataset of patients model, statistically significant differences were observed
with SARS in the study period, 14,732 (5.17%) lacked between black females (aOR = 2.52; p < 0.001) and males
information on diagnostic testing, 94,188 (33.06%) did (aOR = 2.38; p < 0.001).
not have record “race” (missing data) or classified race Table 2 illustrates the interactions between the variables
as “unknown,” 2,525 (0.89%) classified the individual “gender/race” and “education.” The variable “education”
as Asian-descendant and 655 (0.23%) identified as did not yield any changes in effect among white people.
indigenous. Furthermore, 107 (0.04%) observations On the other hand, for the black population, lower levels
were missing information on the variable “gender.” After of education had a more significant impact on the non-
applying the exclusion criteria, the final study population testing of females (aOR = 3.22; p = 0.001) and, to a lesser
comprised 179,295 records. extent, males (aOR = 2.61; p < 0.001) compared to white
As shown in Table 1, more than half of the study males. Higher levels of education reversed the effects on
population comprised males (n = 98,199; 54.77%). Among non-testing in the black population: males displayed a
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 29 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.0865