Page 9 - ITPS-6-2
P. 9
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Theranostics in neurosurgery
inhibited by tumor cells . Utilizing the patient’s own
[18]
immune system against the tumor prevents many side
effects that other foreign agents could cause. FUS-directed
chemotherapy has drastically improved clinical outcomes
for patients with glioblastoma [16,17] . Many studies have
observed increased inflammation and cranial edema after
repeated FUS use, but this finding is dependent on the
parameters of FUS used. For instance, one study by Choi
et al. evaluating an animal model found that 0.25 MPa
of pressure led to no cellular or tissue damage, whereas a
[19]
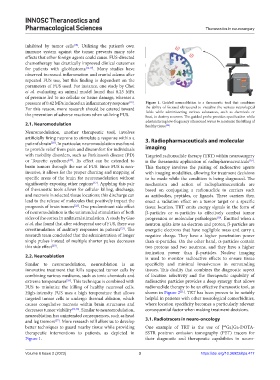
pressure of 0.42 MPa induced an inflammatory response . Figure 1. Guided neuroablation is a theranostic tool that combines
For this reason, more research should be catered toward the ability of focused ultrasound to visualize the various neurological
fields while administering various substances, such as chemicals or
the prevention of adverse reactions when utilizing FUS. heat, to destroy neurons. The guided probe provides specification while
administering low-frequency ultrasound waves to minimize the killing of
2.1. Neuromodulation healthy tissue .
[28]
Neuromodulation, another therapeutic tool, involves
artificially firing neurons to stimulate a response within a 3. Radiopharmaceuticals and molecular
patient’s brain . In particular, neuromodulation was found
[20]
to provide relief from pain and discomfort for individuals imaging
with mobility disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease (PD) Targeted radionuclide therapy (TRT) within neurosurgery
or Tourette syndrome . Its effect can be extended to is the theranostic application of radiopharmaceuticals .
[21]
[29]
brain tumors through the use of FUS. Since FUS is non- This therapy involves the pairing of radioactive agents
invasive, it allows for the proper charting and mapping of with imaging modalities, allowing for treatment decisions
specific areas of the brain for neuromodulation without to be made while the condition is being diagnosed. The
[22]
significantly exposing other regions . Applying this pair mechanism and action of radiopharmaceuticals are
of theranostic tools allows for cellular killing, discharge, based on conjugating a radionuclide to carriers such
and necrosis in selected tissue locations; this discharge can as antibodies, peptides, or ligands. These carriers then
lead to the release of molecules that positively impact the enact a radiation effect on a tumor target or a specific
prognosis of brain tumors . One predominant side effect tissue location. TRT emits energy signals in the form of
[22]
of neuromodulation is the unintended stimulation of both β-particles or α-particles to effectively combat tumor
sides of the cortex in unilateral stimulation. A study by Guo progression or molecular pathologies . Emitted when a
[30]
et al. also found that after widespread use of FUS, there was neutron splits into an electron and proton, β-particles are
overstimulation of auditory responses in patients . The energetic electrons that have negligible mass and carry a
[23]
research team concluded that the administration of longer negative charge. They have a higher penetration power
single pulses instead of multiple shorter pulses decreases than α-particles. On the other hand, α-particles contain
this side effect . two protons and two neutrons, and they have a higher
[23]
ionization power than β-particles. Nuclear imaging
2.2. Neuroablation is used to monitor radioactive effects to ensure tissue
Similar to neuromodulation, neuroablation is an specificity and minimal invasiveness in surrounding
innovative treatment that kills suspected tumor cells by tissues. This duality that combines the diagnostic aspect
combining various mediums, such as toxic chemicals and of location selectivity and the therapeutic capability of
extreme temperatures . This technique is combined with radioactive particles provides a deep synergy that allows
[24]
FUS to minimize the killing of healthy neuronal cells. radionuclide therapy to be an effective theranostic tool, as
High-intensity FUS uses a high temperature that allows shown in Figure 2 . TRT has been proven to be notably
[31]
targeted tumor cells to undergo thermal ablation, which helpful in patients with other neurological comorbidities,
causes coagulative necrosis within brain structures and where location specificity becomes a particularly relevant
decreases tumor viability [25,26] . Similar to neuromodulation, consequential factor when making treatment decisions.
neuroablation has unintended consequences, such as head
and leg tremors . More research will allow us to develop 3.1. Radiotracers in neuro-oncology
[27]
better techniques to guard nearby tissue while providing One example of TRT is the use of [ Ga]Ga-DOTA-
68
therapeutic interventions to patients, as depicted in SSTR positron emission tomography (PET) tracers for
Figure 1. their diagnostic and therapeutic capabilities in neuro-
Volume 6 Issue 2 (2023) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/itps.417