Page 36 - ITPS-7-1
P. 36
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Antiplatelet treatments in neurological patients
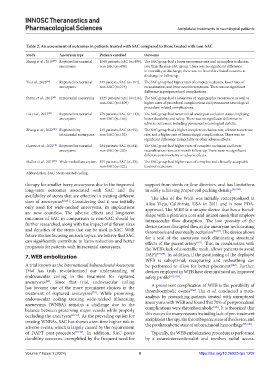
Table 2. An assessment of outcomes in patients treated with SAC compared to those treated with non‑SAC
Study Aneurysm type Patients enrolled Outcome
Zhang et al., 2019 [87] Ruptured intracranial 1049 patients; SAC (n=499), The SAC group had a lower recurrence rate and incomplete occlusion
aneurysms non-SAC (n=409) rate than the non-SAC group. There was no significant difference
in mortality at discharge; there was no favorable clinical outcome at
discharge or follow-up.
Yi et al., 2022 [88] Ruptured intracranial 375 patients; SAC (n=101), The SAC group had higher rates of complete occlusion, lower rates of
aneurysms non-SAC (n=274) recanalization, and lower need for treatment. There was no significant
difference in periprocedural complications.
Piotin et al., 2012 [60] Intracranial aneurysms 1325 patients; SAC (n=216), The SAC group had a lower rate of angiographic recurrence, as well as
non-SAC (n=1109) higher rates of procedural complications and permanent neurological
procedure-related complications.
Liu et al., 2017 [89] Ruptured intracranial 279 patients; SAC (n=113), The SAC group had better initial aneurysm occlusion status, implying
aneurysms non-SAC (n=166) better durability and safety. There was no significant difference in
adverse outcomes, including permanent neurological deficits.
Zhang et al., 2022 [90] Ruptured tiny 245 patients; SAC (n=93), The SAC group had a higher complete occlusion rate, a lower recurrence
intracranial aneurysms non-SAC (n=152) rate, and a higher rate of hemorrhagic complications. There was no
significant difference in mortality or other adverse effects.
Goertz et al., 2021 [91] Ruptured intracranial 284 patients; SAC (n=64), The SAC group had higher rates of complete occlusion and lower
aneurysms non-SAC (n=220) recanalization rates at 6-month follow-up. There were no significant
differences in mortality or adverse effects.
Muller et al., 2017 [92] Wide-necked aneurysms 355 patients; SAC (n=33), The SAC group had higher rates of complete and clinically acceptable
non-SAC (n=322) levels of occlusion.
Abbreviation: SAC: Stent-assisted coiling.
therapy for smaller berry aneurysms due to the improved support from stents or flow diverters, and has limitations
long-term outcomes associated with SAC and the in safely achieving proper coil packing density [99,100] .
availability of stents that are effective in treating different The idea of the WEB was initially conceptualized in
sizes of aneurysms [60,61] . Considering that it was initially Aliso Viejo, California, USA in 2011 and is now FDA-
only used for wide-necked aneurysms, its implications approved. The WEB is a unique device that has a barrel-
are now countless. The adverse effects and long-term shape with a platinum core and nitinol mesh that employs
outcomes of SAC in comparison to non-SAC should be intrasaccular flow disruption. The low porosity of the
further researched, along with the impact of different sizes device causes disrupted flow at the aneurysm neck causing
and densities of the stents that can be used in SAC. With thrombosis and eventually occlusion [93,97] . The device allows
future studies focusing on such topics, we believe that SAC for a seal of the aneurysm neck eliminating structural
can significantly contribute to harm reduction and better effects of the parent artery [101] . This, in combination with
prognosis for patients with intracranial aneurysms. the WEB’s lack of a metallic mesh, allows patients to avoid
7. WEB embolization DAPT [93,99] . In addition, if the positioning of the deployed
WEB is suboptimal, recapturing and resheathing can
A trial known as the International Subarachnoid Aneurysm be performed to allow for better placement [102] . Further,
Trial has truly revolutionized our understanding of devices employed in WEB have demonstrated an improved
endovascular coiling in the treatment for ruptured safety profile [102,103] .
aneurysms . Since that trial, endovascular coiling
[93]
has become one of the more prominent choices in the A prominent complication of WEB is the possibility of
[104]
treatment of ruptured aneurysms . While promising, thromboembolic events . Tau et al. conducted a meta-
[93]
endovascular coiling treating wide-necked bifurcating analysis by researching patients treated with unruptured
aneurysms (WNBA) remains a challenge due to the aneurysms with WEB and found that 70% of periprocedural
[105]
balance between preserving major vessels while properly complications were thromboembolic . It is theorized that
occluding the aneurysm [94-97] . As the prevailing option for this occurs for many reasons including lack of pre-treatment
treating WNBAs, SAC has shown a ten-time higher risk in antiplatelet therapy, the thrombogenic state of the device, and
[93,106]
adverse events, which is largely caused by the requirement the prothrombotic state of subarachnoid hemorrhage .
of DAPT post-procedure [94-99] . In addition, SAC poses Typically, the WEB embolization procedure is performed
durability concerns, exemplified by the frequent need for by a neurointerventionalist and involves radial access.
Volume 7 Issue 1 (2024) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/itps.1202