Page 107 - ITPS-7-2
P. 107
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Molecular docking against SARS-CoV-2
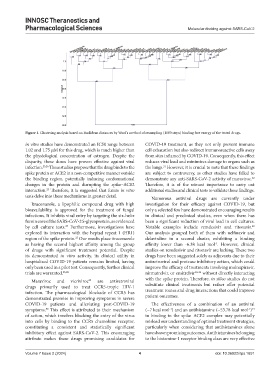
Figure 1. Clustering analysis based on Euclidean distances by Ward’s method of resampling (1000 steps) binding free energy of the tested drugs.
in vitro studies have demonstrated an IC50 range between COVID-19 treatment, as they not only prevent immune
1.02 and 1.75 μM for this drug, which is much higher than cell exhaustion but also redirect immunoreactive cells away
the physiological concentration of estrogen. Despite the from sites inflamed by COVID-19. Consequently, this effect
disparity, these doses have proven effective against viral reduces viral load and minimizes damage to organs such as
infection. 25,26 These studies propose that the drug binds to the the lungs. However, it is crucial to note that these findings
31
spike protein or ACE2 in a non-competitive manner outside are subject to controversy, as other studies have failed to
the binding region, potentially inducing conformational demonstrate any anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity of maraviroc.
32
changes in the protein and disrupting the spike–ACE2 Therefore, it is of the utmost importance to carry out
25
interaction. Therefore, it is suggested that future in vitro additional studies and clinical tests to validate these findings.
tests delve into these mechanisms in greater detail. Numerous antiviral drugs are currently under
Itraconazole, a lipophilic compound drug with high investigation for their efficacy against COVID-19, but
bioavailability, is approved for the treatment of fungal only a selected few have demonstrated encouraging results
infections. It inhibits viral entry by targeting the six-helix in clinical and preclinical studies, even when there has
furoin core of the SARS-CoV-2 S-glycoprotein, as evidenced been a significant reduction of viral load in cell cultures.
by cell culture tests. Furthermore, investigations have Notable examples include remdesivir and ritonavir.
33
27
explored its interaction with the heptad repeat 1 (HR1) Our analysis grouped both of them with nelfinavir and
region of the spike protein. Our results place itraconazole delavirdine in a second cluster, exhibiting a binding
25
-1
as having the second highest affinity among the group affinity lower than -6.38 kcal mol . However, clinical
of drugs with significant treatment potential. Despite studies on remdesivir and ritonavir are lacking. These two
its demonstrated in vitro activity, its clinical utility in drugs have been suggested solely as adjuvants due to their
hospitalized COVID-19 patients remains limited, having antiretroviral and protease inhibitory action, which could
only been used in a pilot test. Consequently, further clinical improve the efficacy of treatments involving molnupiravir,
trials are warranted. 25,28 nirmatrelvir, or ensitrelvir 34-36 without directly interacting
Maraviroc and vicriviroc 29 are antiretroviral with the spike protein. Therefore, in silico studies do not
drugs primarily used to treat CCR5-tropic HIV-1 substitute clinical treatments but rather offer potential
infection. The pharmacological blockade of CCR5 has treatment routes and drug interactions that could improve
demonstrated promise in improving symptoms in severe patient outcomes.
COVID-19 patients and alleviating post-COVID-19 The effectiveness of a combination of an antiviral
symptoms. This effect is attributed to their mechanism (−7 kcal mol ) and an antihistamine (−53.78 kcal mol )
-1
-1 14
30
of action, which involves blocking the entry of the virus in binding to the spike–ACE2 complex may potentially
into cells by binding to the CCR5 chemokine receptor, mislead our understanding of optimal treatment strategies,
constituting a consistent and statistically significant particularly when considering that antihistamines alone
inhibitory effect against SARS-CoV-2. This encouraging have shown promising outcomes. Antihistamines belonging
attribute makes these drugs promising candidates for to the histamine-1 receptor binding class are very effective
Volume 7 Issue 2 (2024) 4 doi: 10.36922/itps.1651