Page 55 - ITPS-7-3
P. 55
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Designing miRNA ONTs for cardiometabolic pandemics
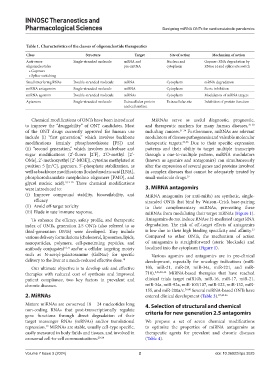
Table 1. Characteristics of the classes of oligonucleotide therapeutics
Class Structure Target Site of action Mechanism of action
Anti-sense Single-stranded molecule mRNA and Nucleus and Gapmer: RNA degradation by
oligonucleotides pre-mRNA cytoplasm RNase H and splice site switch
• Gapmers
• Splice‑switching
Small interfering RNAs Double-stranded molecule mRNA Cytoplasm mRNA degradation
miRNA antagomirs Single-stranded molecule miRNA Cytoplasm Steric inhibition
miRNA agomirs Double-stranded molecule mRNAs Cytoplasm Modulation of mRNA targets
Aptamers Single-stranded molecule Extracellular protein Extracellular site Inhibition of protein function
and cell surface
Chemical modifications of ONTs have been introduced MiRNAs serve as useful diagnostic, prognostic,
to improve the “druggability” of ONT candidates. Most and therapeutic markers for many human diseases, 25-30
of the ONT drugs currently approved for human use including cancers. 31-34 Furthermore, miRNAs are relevant
include (i) “first generation,” which involves backbone modulators of disease pathogenesis and valuable molecular
modifications (mainly phosphorothioate [PS]) and therapeutic targets. 35,36 Due to their specific expression
(ii) “second generation,” which involves nucleobase and patterns and their ability to target multiple transcripts
sugar modifications (2’-fluoro [2’F], 2’O-methyl [2’- through a one-to-multiple pattern, miRNA modulators
OMe], 2’-methoxyethyl [2’-MOE]), cytosine methylated at (known as agomirs and antagomirs) can simultaneously
position 5 [m C], gapmers, 5’-phosphate stabilization, as alter the expression of several genes and proteins involved
5
well as backbone modifications (locked nucleic acid [LNA], in complex diseases that cannot be adequately treated by
phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomers [PMO], and small-molecule drugs. 37
glycol nucleic acid). 9,13-15 These chemical modifications
were introduced to: 3. MiRNA antagomirs
(i) Improve compound stability, bioavailability, and MiRNA antagomirs (or anti-miRs) are synthetic, single-
efficacy stranded ONTs that bind by Watson–Crick base-pairing
(ii) Avoid off-target toxicity to their complementary miRNAs, preventing these
(iii) Elude innate immune response. miRNAs from modulating their target mRNAs (Figure 1).
To enhance the efficacy, safety profile, and therapeutic Antagomirs do not induce RNAse H-mediated target RNA
index of ONTs, generation 2.5 ONTs (also referred to as degradation. The risk of off-target effects of antagomirs
13
third-generation ONTs) were developed. They include is low due to their high binding specificity and affinity.
various delivery formulations (cholesterol, liposomes, lipids, Compared to other ONTs, the mechanism of action
nanoparticles, polymers, cell-penetrating peptides, and of antagomirs is straightforward (steric blockade) and
antibody conjugates) 16,17 and or a cellular targeting moiety localized into the cytoplasm (Figure 1).
/
such as N-acetyl-galactosamine (GalNac) for specific Various agomirs and antagomirs are in pre-clinical
delivery to the liver at a much-reduced effective dose. 18 development, especially for oncology indications (miR-
Our ultimate objective is to develop safe and effective 10b, miR-21, miR-29, miR-34a, miR-221, and miR-
therapies with reduced cost of synthesis and improved 710). 2,36,38-42 MiRNA-based therapies that have reached
patient compliance, two key factors in prevalent and clinical trials target miR10b, miR-16, miR-17, miR-21,
chronic diseases. miR-34a, miR-92a, miR-103/107, miR-122, miR-132, miR-
155, and miR-200a/c. 36,40 Several miRNA-based ONTs have
2. MiRNAs entered clinical development (Table 3). 37,43-46
Mature miRNAs are conserved 18 – 24 nucleotides long 4. Selection of structural and chemical
non-coding RNAs that post-transcriptionally regulate criteria for new generation 2.5 antagomirs
gene functions through direct degradation of their
target messenger RNAs (mRNAs) and/or translational We propose a set of seven chemical modifications
repression. MiRNAs are stable, usually cell-type specific, to optimize the properties of miRNA antagomirs as
19
easily measured in body fluids and tissues, and involved in therapeutic agents for prevalent and chronic diseases
exosomal cell-to-cell communications. 20-24 (Table 4).
Volume 7 Issue 3 (2024) 2 doi: 10.36922/itps.3025