Page 29 - ITPS-7-4
P. 29
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Pediatric drug regulations in India
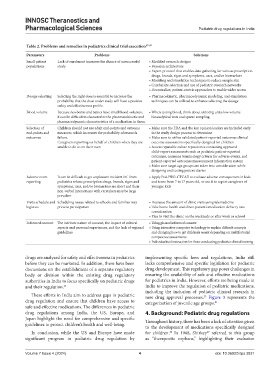
Table 2. Problems and remedies in pediatrics clinical trial execution 67‑69
Parameters Problems Solutions
Small patient Lack of enrolment increases the chance of unsuccessful • Modified research designs
populations study • Bayesian architecture
• Expert protocol that enables data gathering for various prescription
drugs, brands, signs and symptoms, uses, and/or biomarkers
• Modeling and simulation techniques to reduce sample size
• Careful site selection and use of pediatric research networks
• Decentralize, patient‑centric approaches to enable wider access
Dosage selecting Selecting the right dose is essential to increase the • Pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic modeling, and simulation
probability that the dose under study will have a positive techniques can be utilized to enhance selecting the dosage
safety and effectiveness profile.
Blood volume Because newborns and babies have small blood volumes, • When testing blood, think about utilizing ultra‑low volume
it can be difficult to characterize the pharmacokinetic and bioanalytical tests and sparse sampling.
pharmacodynamic characteristics of a medication in them.
Selection of Children should not use adult end-points and outcome • Make sure the FDA and the key opinion leaders are included early
end-points and measures, which increases the probability of research in the study design process to determine
outcomes failure. • Make sure to utilize validated patient‑reported outcomes clinical
Caregivers reporting on behalf of children when they are outcome assessments specifically designed for children
unable to do so on their own • Access reputable online repositories containing approved
child-report assessments such as pediatric patient-reported
outcomes, common terminology criteria for adverse events, and
patient-reported outcomes measurement information system
• Make sure target age groups are taken into consideration while
designing and testing patient diaries
Adverse event It can be difficult to get unpleasant incident inf. from • Apply Ped‑PRO‑CTCAE to evaluate adverse consequences in kids
reporting pediatrics whose prescription drugs, brands, signs and and teens from 7 to 17 years old, or use it to report caregivers of
symptoms, uses, and/or biomarkers are short and their younger kids
non-verbal interactions with caretakers may be large
prevalent
Visits schedule and Scheduling issues related to schools and families may • Decrease the amount of clinic visits using telemedicine
logistics prevent participation • Take home health and direct patient’s medication delivery into
consideration
• Plan to visit the clinic on the weekends or after work or school
Informed consent The intricate nature of consent, the impact of cultural • Using phased informed consent
aspects and personal experiences, and the lack of regional • Using interactive computer technology to explain difficult concepts
guidelines and changing how to get children’s assent depending on multifactorial
competence assessments
• Individualized instruction for those conducting pediatrics clinical training
drugs are analyzed for safety and effectiveness in pediatrics implementing specific laws and regulations, India still
before they can be marketed. In addition, there have been lacks comprehensive and specific legislation for pediatric
discussions on the establishment of a separate regulatory drug development. This regulatory gap poses challenges in
body or division within the existing drug regulatory ensuring the availability of safe and effective medications
authorities in India to focus specifically on pediatric drugs for pediatrics in India. However, efforts are being made in
and their regulation. 24 India to improve the regulation of pediatric medications,
including the inclusion of pediatric clinical research in
These efforts in India aim to address gaps in pediatric new drug approval processes. Figure 3 represents the
25
drug regulation and ensure that children have access to categorization of juvenile age groups. 21
safe and effective medications. The differences in pediatric
drug regulations among India, the US, Europe, and 4. Background: Pediatric drug regulations
Japan highlight the need for comprehensive and specific
guidelines to protect children’s health and well-being. Throughout history, there has been a lack of attention given
to the development of medications specifically designed
In conclusion, while the US and Europe have made for children. In 1968, Shirkey referred to this group
27
26
significant progress in pediatric drug regulation by as “therapeutic orphans,” highlighting their exclusion
Volume 7 Issue 4 (2024) 4 doi: 10.36922/itps.3831