Page 51 - ITPS-7-4
P. 51
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Biomarkers and drugs in Africa
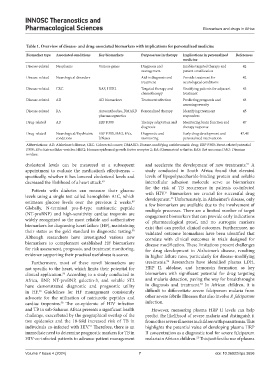
Table 1. Overview of disease- and drug-associated biomarkers with implications for personalized medicine
Biomarker type Associated conditions Key biomarkers Purpose/use in therapy Implications in personalized References
medicine
Disease-related Neoplasms Various genes Diagnosis and Enables targeted therapy and 42
management patient stratification
Disease-related Neurological disorders ----- Aid in diagnosis and Provide treatment for 42
treatment neurological conditions
Disease-related CRC RAS, HER2 Targeted therapy and Stratifying patients for adjuvant 43
chemotherapy treatment
Disease-related AD AD biomarkers Treatment selection Predicting prognosis and 44
assessing severity
Disease-related RA Autoantibodies, DMARD Personalized therapy Identifying treatment 45
pharmacogenetics responders
Drug-related AD ERP P300 Therapy adaptation and Monitoring brain function and 47
diagnosis therapy response
Drug-related Neurological/Psychiatric ERP P300, DAO, EVs, Diagnostic and Early drug development and 47,48
conditions DNases monitoring personalized intervention
Abbreviations: AD: Alzheimer’s disease; CRC: Colorectal cancer; DMARD: Disease-modifying antirheumatic drug; ERP P300: Event-related potential
P300; EVs: Extracellular vesicles; HER2: Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; RA: Rheumatoid arthritis; RAS: Rat sarcoma; DAO: Diamine
oxidase.
cholesterol levels can be measured at a subsequent and accelerate the development of new treatments. A
51
appointment to evaluate the medication’s effectiveness – study conducted in South Africa found that elevated
specifically, whether it has lowered cholesterol levels and levels of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein and soluble
decreased the likelihood of a heart attack. 49 intercellular adhesion molecule serve as biomarkers
for the risk of TB recurrence in patients co-infected
Patients with diabetes can measure their glucose with HIV. Biomarkers are crucial for successful drug
51
levels using a single test called hemoglobin A1C, which development. Unfortunately, in Alzheimer’s disease, only
33
estimates glucose levels over the previous 2 weeks. a few biomarkers are available due to the involvement of
49
Globally, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide multiple processes. There are a limited number of target
(NT-proBNP) and high-sensitivity cardiac troponin are engagement biomarkers that can provide early indications
widely recognized as the most reliable and authoritative of pharmacological proof, and no surrogate markers
biomarkers for diagnosing heart failure (HF), maintaining exist that can predict clinical outcomes. Furthermore, no
their status as the gold standard in diagnostic testing. validated outcome biomarkers have been identified that
50
Although researchers have investigated various new correlate with clinical outcomes in trials designed for
biomarkers to complement established HF biomarkers disease modification. These limitations present challenges
for risk assessment, prognosis, and treatment monitoring, for drug development in Alzheimer’s disease, resulting
evidence supporting their practical usefulness is scarce. in higher failure rates, particularly for disease-modifying
52
Furthermore, most of these novel biomarkers are treatments. Researchers have identified plasma LDH,
not specific to the heart, which limits their potential for HRP II, aldolase, and hemozoin formation as key
50
clinical application. According to a study conducted in biomarkers with significant potential for drug targeting
Africa, BNP, NT-proBNP, galectin-3, and soluble ST2 and malaria detection, paving the way for breakthroughs
53
have demonstrated diagnostic and prognostic utility in diagnosis and treatment. In African children, it is
in HF. Guidelines for HF management consistently difficult to differentiate severe falciparum malaria from
50
advocate for the utilization of natriuretic peptides and other severe febrile illnesses that also involve P. falciparum
cardiac troponins. The co-epidemic of HIV infection infection.
50
and TB in sub-Saharan Africa presents a significant health However, measuring plasma HRP II levels can help
challenge, exacerbated by the geographical overlap of the predict the likelihood of severe malaria and distinguish it
two epidemics and the 18-fold increased risk of TB in from other severe illnesses in children with parasitemia. This
individuals co-infected with HIV. Therefore, there is an highlights the potential value of developing plasma HRP
51
immediate need to determine prognostic markers for TB in II concentration as a diagnostic tool for severe falciparum
HIV-co-infected patients to advance patient management malaria in African children. This justifies the use of plasma
53
Volume 7 Issue 4 (2024) 7 doi: 10.36922/itps.3656