Page 52 - ITPS-7-4
P. 52
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Biomarkers and drugs in Africa
HRP II concentration as a biomarker for assessing severe efforts are being made to include African genetic diversity
falciparum malaria in this population. Several deaths in global genomic data, a lack of skilled personnel hinders
53
from communicable and non-communicable diseases the storage, retrieval, analysis, and interpretation of
occur in low- and middle-income countries due to a lack clinical, epidemiological, and genomic data. Biomarkers
48
of early diagnosis and treatment. Biomarkers can help by are essential for developing targeted therapies and
48
serving as indicators of disease conditions or treatment personalized treatment plans, particularly in Africa,
responses. However, results from developed countries may where healthcare disparities and disease burdens present
not be directly applicable to developing countries owing unique challenges. By identifying biomarkers specific to
to differences in disease patterns. Biomarker candidates the African population or reflecting regional variations in
48
identified through advanced technology hold potential; disease pathology, researchers and healthcare professionals
however, their application is hindered by challenges such can tailor interventions and accelerate the approval process
as disease heterogeneity and pre-analytical variability. for novel therapeutics. This is particularly important in
48
Economic constraints, a lack of education and awareness, the African context, where efficient drug development
and various social and ethical issues also hinder biomarker processes are crucial for delivering innovative treatments
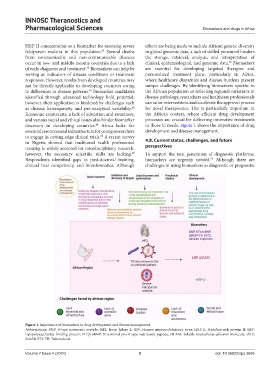
discovery in developing countries. Africa lacks the to those in needs. Figure 1 shows the importance of drug
48
essential resources and infrastructure for young researchers development and disease management.
to engage in cutting-edge clinical trials. A recent survey
48
in Nigeria showed that traditional health professional 4.8. Current status, challenges, and future
training is widely accepted for interdisciplinary research; perspectives
however, the necessary scientific skills are lacking. To support the next generation of diagnostic platforms,
48
54
Respondents identified gaps in post-doctoral training, biomarkers are urgently needed. Although there are
clinical trial competency, and bioinformatics. Although challenges in using biomarkers as diagnostic or prognostic
Figure 1. Importance of biomarkers in drug development and disease management
Abbreviations: BNP: B-type natriuretic peptide; HF2: Heart failure 2; HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus; HRP II: Histidine-rich protein II; LBP:
Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein; NT-proBNP: N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide; sICAM: Soluble intercellular adhesion molecule; sST2:
Soluble ST2; TB: Tuberculosis.
Volume 7 Issue 4 (2024) 8 doi: 10.36922/itps.3656