Page 97 - ITPS-7-4
P. 97
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences LMWH for VTE prophylaxis in acute stroke patients
• Group B consists of 752 patients admitted between
August 1, 2022, and July 31, 2023 (12 months). The
patients in this group used LMWH (enoxaparin 20
– 40 mg delivered subcutaneously, dose adjusted for
weight) as VTE prophylaxis during the admission
period for acute stroke.
In each of the groups, the patients who developed PE,
DVT, or symptomatic HT within 3 months of their stroke
were identified. They were investigated if they presented
with clinical symptoms or were suspected of PE/DVT or
symptomatic HT. The diagnosis of ischemic stroke, PE,
DVT, and HT was confirmed by radiological means such
as computed tomography (CT) of the head, CT pulmonary
angiogram, and Doppler ultrasound.
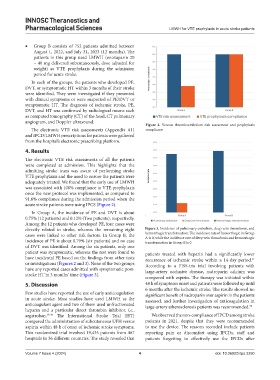
Figure 2. Venous thromboembolism risk assessment and prophylaxis
The electronic VTE risk assessments (Appendix A1) compliance
and IPCD/LMWH prescriptions for patients were gathered
from the hospital’s electronic prescribing platform.
4. Results
The electronic VTE risk assessments of all the patients
were completed at admission. This highlights that the
admitting stroke team was aware of performing stroke
VTE prophylaxis and the need to ensure the patients were
adequately treated. We found that the early use of LMWH
was associated with 100% compliance to VTE prophylaxis
once the new protocol was implemented, as compared to
91.6% compliance during the admission period when the
acute stroke patients were using IPCS (Figure 2).
In Group A, the incidence of PE and DVT is about
0.75% (12 patients) and 0.12% (Two patients), respectively.
Among the 12 patients who developed PE, four cases were
directly related to stroke, whereas the remaining eight Figure 3. Incidence of pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, and
cases were linked to other risk factors. In Group B, the hemorrhagic transformation. The incidence rate of hemorrhagic in Group
A is 0, while the incidence rate of deep vein thrombosis and hemorrhagic
incidence of PE is about 0.79% (six patients) and no case transformation in Group B is 0
of DVT was identified. Among the six patients, only one
patient was symptomatic, whereas the rest were found to patients treated with heparin had a significantly lower
have incidental PE based on the findings from other tests recurrence of ischemic stroke within a 14-day period.
31
or investigations (Figures 2 and 3). None of the two groups According to a FISS-tris trial involving patients with
have any reported cases admitted with symptomatic post- large-artery occlusive disease, nadroparin calcium was
stroke HT in 3 months’ time (Figure 3).
compared with aspirin. The therapy was initiated within
5. Discussion 48 h of symptoms onset and patients were followed up until
6 months after the ischemic stroke. The results showed no
Few studies have reported the use of early anticoagulation significant benefit of nadroparin over aspirin in the patients
in acute stroke. Most studies have used LMWH as the assessed, and further investigation of anticoagulation in
anticoagulant agent and two of them used unfractionated large-artery atherosclerosis patients was recommended. 32
heparin and a particular direct thrombin inhibitor, i.e.,
argatroban. 28-30 The International Stroke Trial (IST) We observed the non-compliance of IPCD among stroke
compared the administration of subcutaneous UFH versus patients in 2021, despite that they were recommended
aspirin within 48 h of onset of ischemic stroke symptoms. to use the device. The reasons recorded include patients
This randomized trial involved 19,435 patients from 467 reporting pain or discomfort using IPCDs, staff and
hospitals in 36 different countries. The study revealed that patients forgetting to effectively use the IPCDs after
Volume 7 Issue 4 (2024) 4 doi: 10.36922/itps.3250