Page 25 - ITPS-8-2
P. 25
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences The biochemical and biophysical guide for photodynamic therapy
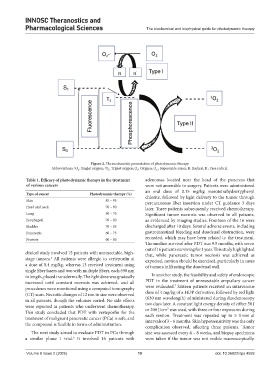
Figure 2. The mechanistic presentation of photodynamic therapy
·
Abbreviations: O : Singlet oxygen; O : Triplet oxygen; O : Oxygen; O : Superoxide anion; R: Radical; R : Free radical.
1
-
3
2 2 2 2
Table 1. Efficacy of photodynamic therapy in the treatment adenomas located near the head of the pancreas that
of various cancers were not amenable to surgery. Patients were administered
an oral dose of 0.15 mg/kg mesotetrahydroxyphenyl
Type of cancer Photodynamic therapy (%) chlorite, followed by light delivery to the tumor through
Skin 85 – 95 percutaneous fiber insertion under CT guidance 3 days
Head and neck 70 – 90 later. Three patients subsequently received chemotherapy.
Lung 50 – 70 Significant tumor necrosis was observed in all patients,
Esophageal 70 – 80 as evidenced by imaging studies. Fourteen of the 16 were
Bladder 70 – 85 discharged after 10 days. Several adverse events, including
Pancreatic 60 – 75 gastrointestinal bleeding and duodenal obstruction, were
recorded, which may have been related to the treatment.
Prostate 60 – 80
The median survival after PDT was 9.5 months, with seven
out of 16 patients surviving for 1 year. This study highlighted
clinical study involved 15 patients with unresectable, high- that, while pancreatic tumor necrosis was achieved as
stage tumors. All patients were allergic to verteporfin at expected, caution should be exercised, particularly in cases
5
a dose of 0.4 mg/kg, whereas 13 received treatment using of tumors infiltrating the duodenal wall.
single fiber lasers and two with multiple fibers, each 690 nm
in length, placed transdermally. The light dose was gradually In another study, the feasibility and safety of endoscopic
increased until constant necrosis was achieved, and all PDT in the treatment of unresectable ampullary cancer
7
procedures were monitored using a computed tomography were evaluated. Sixteen patients received an intravenous
(CT) scan. Necrotic changes of 12 nm in size were observed dose of 4 mg/kg of a HDP derivative, followed by red light
in all patients, though the volumes varied. No side effects (630 nm wavelength) administered during duodenoscopy
were reported in patients who underwent chemotherapy. two days later. A constant light energy density of either 50 J
This study concluded that PDT with verteporfin for the or 200 J/cm² was used, with three or four exposures during
treatment of malignant pancreatic cancer (PCa) is safe, and each session. Treatment was repeated up to 5 times at
intervals of 3 – 6 months. Skin hypersensitivity was the only
the compound is flexible in terms of administration.
complication observed, affecting three patients. Tumor
The next study aimed to evaluate PDT in PCa through size was assessed every 4 – 8 weeks, and biopsy specimens
a similar phase 1 trial. It involved 16 patients with were taken if the tumor was not visible macroscopically.
6
Volume 8 Issue 2 (2025) 19 doi: 10.36922/itps.4559