Page 56 - ITPS-8-2
P. 56
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Management of heart failure in Pakistan
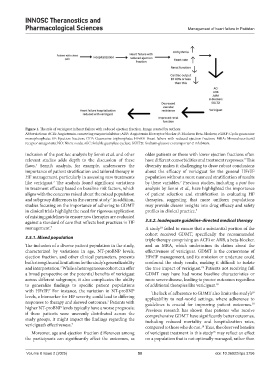
Figure 1. The role of vericiguat in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Image created by authors.
Abbreviations: ACEi: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB: Angiotensin II receptor blocker; B-blockers: Beta-blockers; cGMP: Cyclic guanosine
monophosphate; EF: Ejection fraction; GTP: Guanosine triphosphate; HFrEF: Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction; MRA: Mineralocorticoid
receptor antagonists; NO: Nitric oxide; sGC: Soluble guanylate cyclase; SGLT2i: Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors.
inclusion of the post hoc analysis by Senni et al. and other older patients or those with lower ejection fractions often
relevant studies adds depth to the discussion of these have different comorbidities and treatment responses. This
7
flaws. Senni’s analysis, for example, underscores the diversity makes it challenging to draw robust conclusions
7
importance of patient stratification and tailored therapy in about the efficacy of vericiguat for the general HFrEF
HF management, particularly in assessing new treatments population without a more nuanced stratification of results
like vericiguat. The analysis found significant variations by these variables. Previous studies, including a post hoc
7
7
in treatment efficacy based on baseline risk factors, which analysis by Senni et al., have highlighted the importance
aligns with the concerns raised about the mixed population of patient selection and stratification in evaluating HF
and subgroup differences in the current study. In addition, therapies, suggesting that more uniform populations
7
studies focusing on the importance of adhering to GDMT may provide clearer insights into drug efficacy and safety
in clinical trials highlight the need for rigorous application profiles in clinical practice. 7
of existing guidelines to ensure new therapies are evaluated
against a standard of care that reflects best practices in HF 3.5.2. Inadequate guideline-directed medical therapy
management. 7 A study failed to ensure that a substantial portion of the
18
cohort received GDMT, specifically the recommended
3.5.1. Mixed population triple therapy comprising an ACEi or ARB, a beta-blocker,
The inclusion of a diverse patient population in the study, and an MRA, which undermines its claims about the
characterized by variations in age, NT-proBNP levels, effectiveness of vericiguat. GDMT is the cornerstone of
ejection fraction, and other clinical parameters, presents HFrEF management, and its omission or underuse could
both strengths and limitations for the study’s generalizability confound the study results, making it difficult to isolate
and interpretation. While a heterogeneous cohort can offer the true impact of vericiguat. Patients not receiving full
18
7
a broad perspective on the potential benefits of vericiguat GDMT may have had worse baseline characteristics or
across different subgroups, it also complicates the ability more severe disease, leading to poorer outcomes regardless
to generalize findings to specific patient populations of additional therapies like vericiguat. 18
7
with HFrEF. For instance, the variation in NT-proBNP The lack of adherence to GDMT also limits the study’s
18
levels, a biomarker for HF severity, could lead to differing applicability to real-world settings, where adherence to
responses to therapy and skewed outcomes. Patients with guidelines is crucial for improving patient outcomes.
7
18
higher NT-proBNP levels typically have a worse prognosis; Previous research has shown that patients who receive
if these patients were unevenly distributed across the comprehensive GDMT have significantly better outcomes,
study groups, it might impact the findings regarding the including reduced mortality and hospitalization rates,
vericiguat’s effectiveness. 7 compared to those who do not. Thus, the observed benefits
18
Moreover, age and ejection fraction differences among of vericiguat treatment in this study may reflect an effect
18
the participants can significantly affect the outcomes, as on a population that is not optimally managed, rather than
Volume 8 Issue 2 (2025) 50 doi: 10.36922/itps.3756