Page 10 - ITPS-8-3
P. 10
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences AI in medical device safety
3. Transformation of materiovigilance
through AI
AI is significantly transforming medical device
surveillance by enhancing the processes of monitoring,
diagnosis, and health management. Core AI technologies,
including computer vision (CV), ML, artificial neural
networks, and data fusion techniques, are central to these
advancements. 17,18 The vast amounts of data generated by
real-time sensor measurements, which are essential to
medical devices, have made it possible to extract valuable
19
insights using ML and neural networks. These tools are
crucial for accurate diagnosis, effective supervision of
medical devices, and real-time monitoring.
In addition to these technologies, NLP plays a key role
in analyzing patient data and medical records, whereas CV
is essential for interpreting visual data, including images
and videos. 20,21 In addition, the integration of blockchain
technology with AI is enhancing data security, addressing
issues of data integrity and authenticity, particularly
within health-care settings. This combination ensures the
5
authenticity of acquired data, thereby strengthening the
reliability of medical device surveillance.
The integration of blockchain, NLP, ML, and CV is
driving significant progress in medical device surveillance.
Together, these technologies improve the precision of device
monitoring, enhance diagnostic capabilities, and ensure
the confidentiality and integrity of medical data. As AI
technology continues to evolve, its applications are expected
to expand into areas such as global pandemic forecasting,
personalized medicine, and predictive health care. 22,23
AI enhances data processing, model training, and
software implementation in the context of medical
24
devices. These applications improve patient outcomes,
reduce the burden on health-care providers, and increase
25
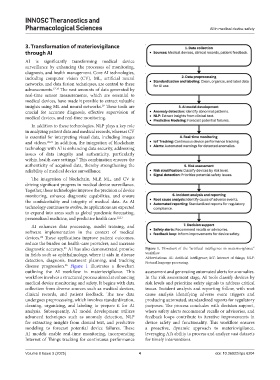
diagnostic accuracy. AI has also demonstrated promise Figure 1. Flowchart of the “artificial intelligence in materiovigilance”
in fields such as ophthalmology, where it aids in disease workflow
Abbreviations: AI: Artificial intelligence; IoT: Internet of things; NLP:
detection, diagnosis, treatment planning, and tracking Natural language processing.
26
disease progression. Figure 1 illustrates a flowchart
outlining the AI workflow in materiovigilance. This assessment and generating automated alerts for anomalies.
workflow involves a structured process aimed at enhancing In the risk assessment stage, AI tools classify devices by
medical device monitoring and safety. It begins with data risk levels and prioritize safety signals to address critical
collection from diverse sources such as medical devices, issues. Incident analysis and reporting follow, with root
clinical records, and patient feedback. The raw data cause analysis identifying adverse event triggers and
undergoes preprocessing, which involves standardization, producing automated, standardized reports for regulatory
cleaning, organizing, and labeling to prepare it for AI purposes. The process concludes with decision support,
analysis. Subsequently, AI model development utilizes where safety alerts recommend recalls or advisories, and
advanced techniques such as anomaly detection, NLP feedback loops contribute to iterative improvements in
for extracting insights from clinical text, and predictive device safety and functionality. This workflow ensures
modeling to forecast potential device failures. These a proactive, dynamic approach to materiovigilance,
AI models enable real-time monitoring, incorporating leveraging AI’s ability to process and analyze vast datasets
Internet of Things tracking for continuous performance for timely interventions.
Volume 8 Issue 3 (2025) 4 doi: 10.36922/itps.6204