Page 25 - JCAU-5-3
P. 25
Journal of Chinese
Architecture and Urbanism Development of industrial heritage reuse modes
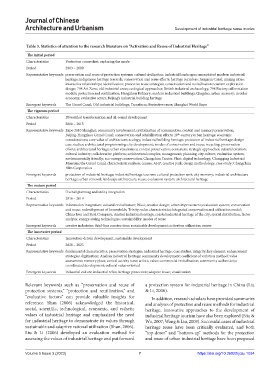
Table 3. Statistics of attention to the research literature on “Activation and Reuse of Industrial Heritage”
The initial period
Characteristics Protection comes first, exploring the mode
Period 2003 – 2009
Representative keywords preservation and reuse of protection systems; cultural civilization; industrial landscapes; unexploited modern industrial
heritage; indigenous heritage research; conservation and reuse efforts; heritage corridors; Jiangnan Canal; mining cities;
interactive relationships; identification; protective reuse strategies; conservation and revitalization; tourism exploration
design; 798 Art Zone; old industrial areas; ecological approaches; British industrial archaeology; 798 Factory; afforestation
models; protection and reutilization; Hangzhou Refinery; modern industrial buildings; Qingdao; urban memory; circular
economy; evaluative actors; Beijing’s industrial building heritage
Emergent keywords The Grand Canal; Old industrial buildings; Transform; Protective reuse; Shanghai World Expo
The vigorous period
Characteristics Diversified transformation and all-round development
Period 2010 – 2015
Representative keywords Expo 2010 Shanghai; community involvement; revitalization of communities; context and memory preservation;
Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal; conservation and rehabilitation efforts; 20 -century urban heritage; economic
th
considerations; core value of architecture; ecology; industrial building heritage; protection of industrial heritage; design
case studies; architectural programming; city development; modes of conservation and reuse; recycling; preservation
efforts; architectural heritage; urban renaissance; context preservation; ecosystem; strategic approaches; cultural creation;
cultural industry; collaborative platform; architectural complex; management; planning; city culture; evaluation system;
environmentally friendly; eco-energy conservation; Changchun Tractor Plant; digital technology; Chongqing Industrial
Museum; the Grand Canal; characteristic analysis; census; AHP; creative park; design methodology; case study; Changchun
Film Corporation
Emergent keywords protection of industrial heritage; industrial heritage tourism; cultural protection unit; city memory; industrial architecture
heritage; urban renewal; landscape architecture; reuse; evaluation system; architectural heritage
The mature period
Characteristics Overall planning and utility integration
Period 2016 – 2019
Representative keywords information integration; cultural revitalization; Wuxi; creative design; urban improvement; evaluation system; conservation
and reuse; redevelopment of brownfields; Trinity; value characteristics; integrated conservation and utilization model;
China Iron and Steel Company; Ansteel industrial heritage; coastal industrial heritage of the city; spatial distribution; factor
analysis; energy-saving technologies; sustainability; modes of reuse
Emergent keywords creative industries; third-line construction; sustainable development; activation utilization; renew
The innovative period
Characteristics Innovation-driven development, sustainable development
Period 2020 – 2023
Representative keywords fundamental characteristics; preservation strategies; industrial heritage; case studies; integrity; key element; enhancement
strategies; digitization; Anshan industrial heritage; community development; coefficient of variation method; value
assessment; memory place; central activity zone; artistic value; commercial revitalization; community authenticity;
coordinated development; cultural value-oriented
Emergent keywords industrial culture; industrial relics; heritage protection; adaptive reuse; visualization
Relevant keywords such as “preservation and reuse of a protection system for industrial heritage in China (Liu
protection systems,” “protection and reutilization,” and & Li, 2006).
“evaluative factors” can provide valuable insights for In addition, research scholars have provided summaries
reference. Shan (2006) acknowledged the historical, and analyses of protection and reuse methods for industrial
social, scientific, technological, economic, and esthetic heritage. Innovative approaches to the development of
values of industrial heritage and emphasized the need industrial heritage tourism have also been explored (Niu &
for industrial heritage to demonstrate its values through Wu, 2007; Wang & Liu, 2009). Successful cases of industrial
sustainable and adaptive rational utilization (Shan, 2006). heritage reuse have been critically evaluated, and both
Liu & Li (2006) developed an evaluation method for “top-down” and “bottom-up” methods for the protection
assessing the values of industrial heritage and put forward and reuse of urban industrial heritage have been proposed
Volume 5 Issue 3 (2023) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcau.1034