Page 79 - JCAU-6-2
P. 79
Journal of Chinese
Architecture and Urbanism Stakeholder perspectives on BRTEMIP
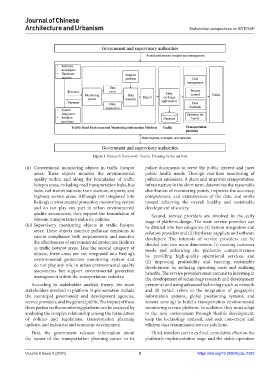
Figure 1. Research framework. Source: Drawing by the authors
(ii) Conventional monitoring objects in traffic hotspot policy documents to serve the public interest and meet
areas: These objects monitor the environmental public health needs. Through real-time monitoring of
quality within and along the boundaries of traffic pollutant emissions, it plans and improves transportation
hotspot areas, including road transportation hubs, bus infrastructure in the short term, determines the reasonable
hubs, rail transit stations, train stations, airports, and distribution of monitoring points, improves the accuracy,
highway service areas. Although not integrated into completeness, and extensiveness of the data, and works
Beijing’s environmental protection monitoring system toward achieving the overall healthy and sustainable
and do not play any part in urban environmental development of society.
quality assessments, they support the formulation of Second, service providers are involved in the early
relevant transportation industry policies. stage of platform design. The main service providers can
(iii) Supervisory monitoring objects in traffic hotspot be divided into two categories: (i) System integrators and
areas: These objects monitor pollutant emissions to solution providers and (ii) hardware suppliers and software
ensure compliance with requirements and monitor developers. The interests of service providers can be
the effectiveness of environmental protection facilities divided into two main dimensions: (i) meeting customer
in traffic hotspot areas. Like the second category of needs and enhancing the platform’s competitiveness
objects, these areas are not integrated into Beijing’s by providing high-quality operational services, and
environmental protection monitoring system and (ii) improving profitability and ensuring sustainable
do not play any role in urban environmental quality development by reducing operating costs and realizing
assessments but support environmental protection benefits. The service providers must commit to investing in
management within the transportation industry. the development of technology research and development
According to stakeholder analysis theory, the main personnel and using advanced technology such as network
stakeholders involved in platform implementation include and 3S (which refers to the integration of geographic
the municipal government and development agencies, information systems, global positioning systems, and
service providers, and the general public. The impact of these remote sensing) to build a transportation environmental
three parties on the monitoring platform can be analyzed by monitoring service platform. In addition, they must adapt
analyzing the complex relationship among the formulation to the new environment through flexible development,
of policies and regulations, transportation planning keep the technology updated, and seek convenient and
updates, and industrial and economic development. efficient data transmission service solutions.
First, the government releases information about Third, travelers exert a cyclical, cumulative effect on the
the layout of the transportation planning center in its platform’s implementation stage and the stable operation
Volume 6 Issue 2 (2024) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcau.2283